Examples
Space weather of Mercury
A global 3D hybrid simulation (RHybrid) of the Hermean solar wind interaction and the formation of the solar wind ion foreshock and ULF waves. (doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3257)
Solar wind driven heavy ion escape from Mars
A global 3D hybrid simulation (RHybrid) of the Martian solar wind driven heavy ion escape and its coupling with the foreshock ULF waves. A comparison of the nominal solar wind case (bottom) to the radial interplanetary magnetic field case (top).
Space weather of Mars
A global 3D hybrid simulation (RHybrid) of the Martian solar wind interaction and the formation of the solar wind ion foreshock and ULF waves. A comparison of the nominal solar wind case (right) to the radial interplanetary magnetic field case (left).
Space weather of Venus
A global 3D hybrid simulation (RHybrid) of the Venusian solar wind interaction and the formation of the solar wind ion foreshock and ULF waves and their coupling with the solar wind driven heavy ion escape. (doi:10.1029/2020GL087462)
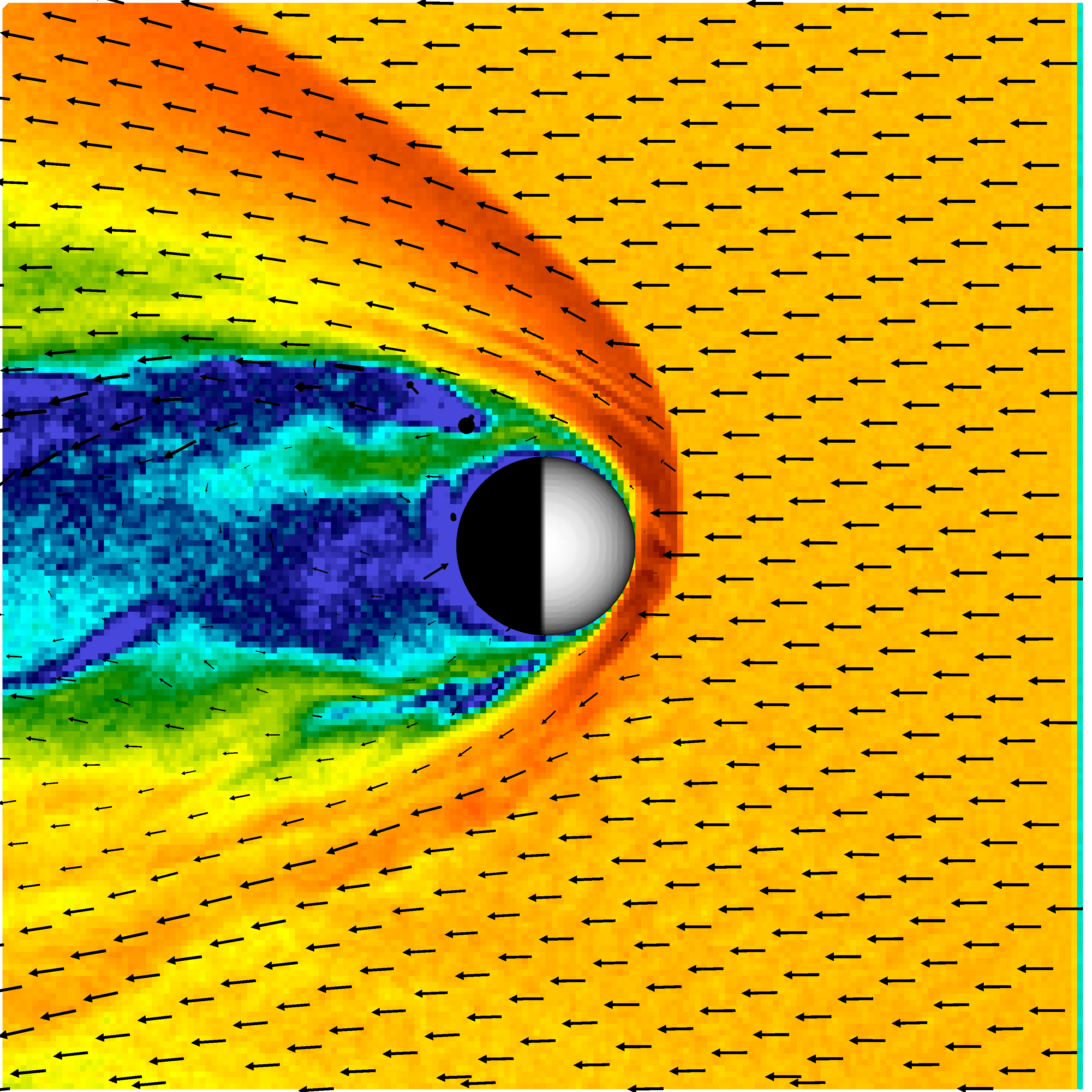
Solar wind flow near Mercury
Ion density and flow vectors of the solar wind in Mercury's magnetospheric solar wind interaction. (doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3257)
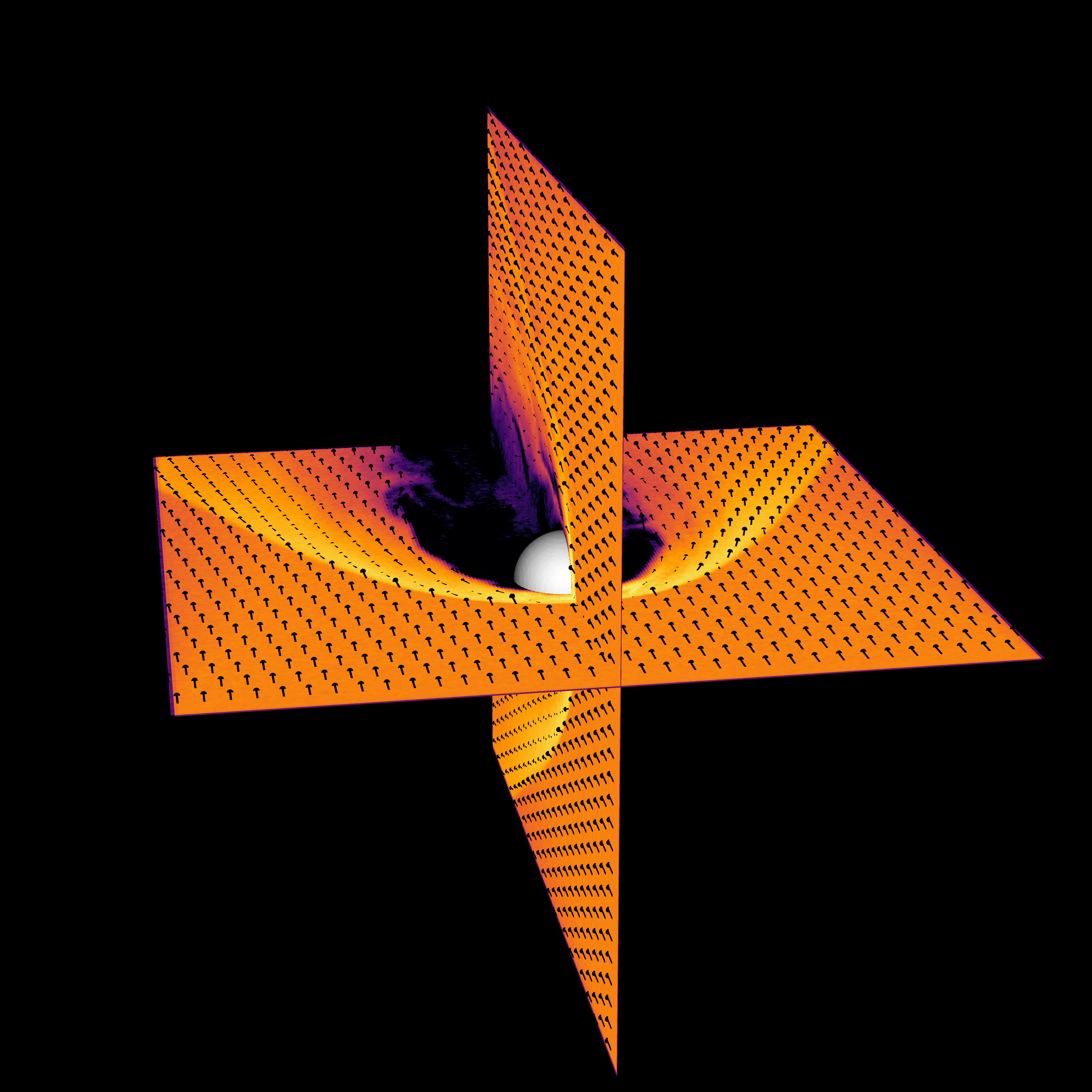
Mercury's magnetosphere and ion foreshock
Formation of the Hermean magnetosphere interaction and the ULF wave foreshock (orange). (doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3257)
Mercury's magnetospheric currents
Electric current density in the Hermean magnetosphere.
Solar wind flow around Mercury
The flow of solar wind ions in Mercury's magnetosphere in the ecliptic.
Mercury's quasi-parallel bow shock
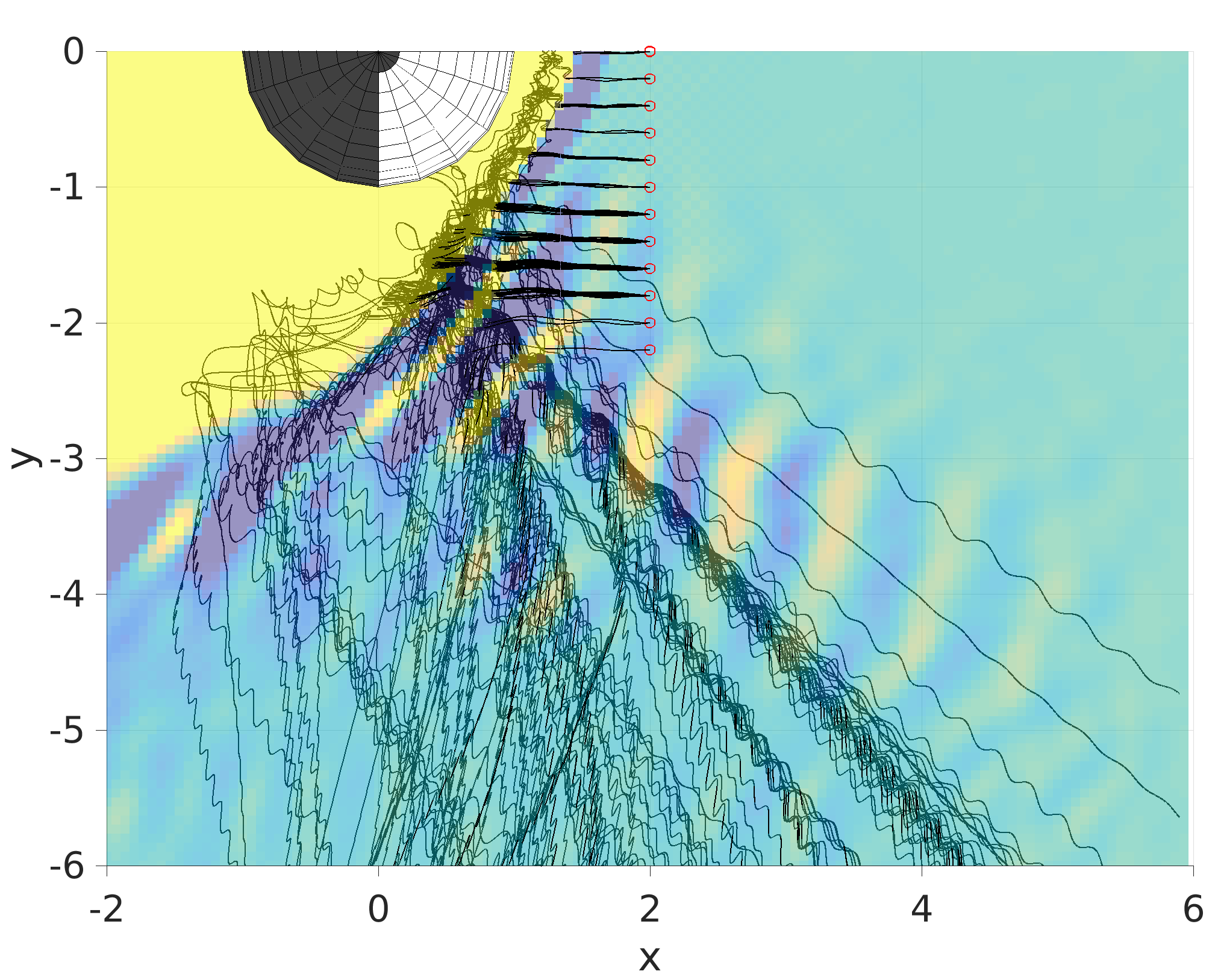
Scattering of the solar wind ions in the quasi-parallel Hermean bow shock and the formation of ion foreshock and ULF waves. (doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3257)
Ion velocity distributions in Mercury's foreshock
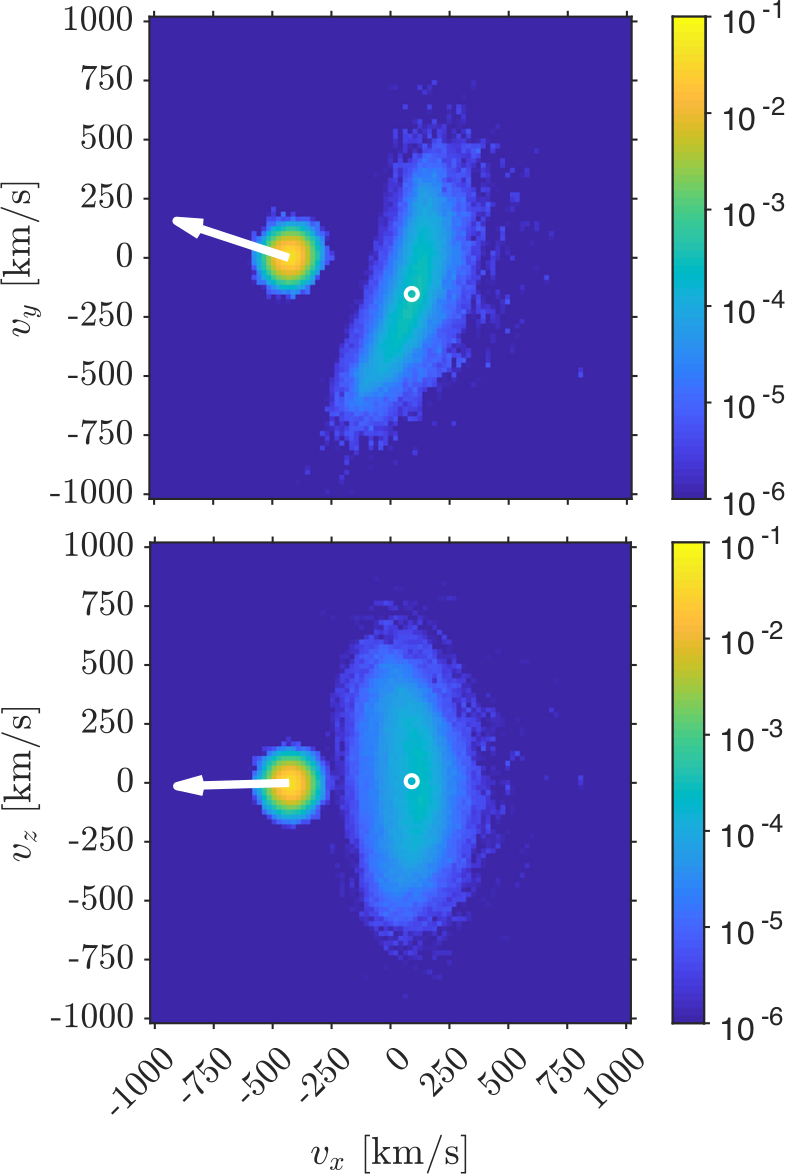
Velocity distributions of the solar wind ions in the 3D RHybrid simulation of the formation of the Hermean foreshock. (doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3257)
Magnetic field draping at Mercury
Draping and connection of the interplanetary magnetic field lines around Mercury's magnetosphere.
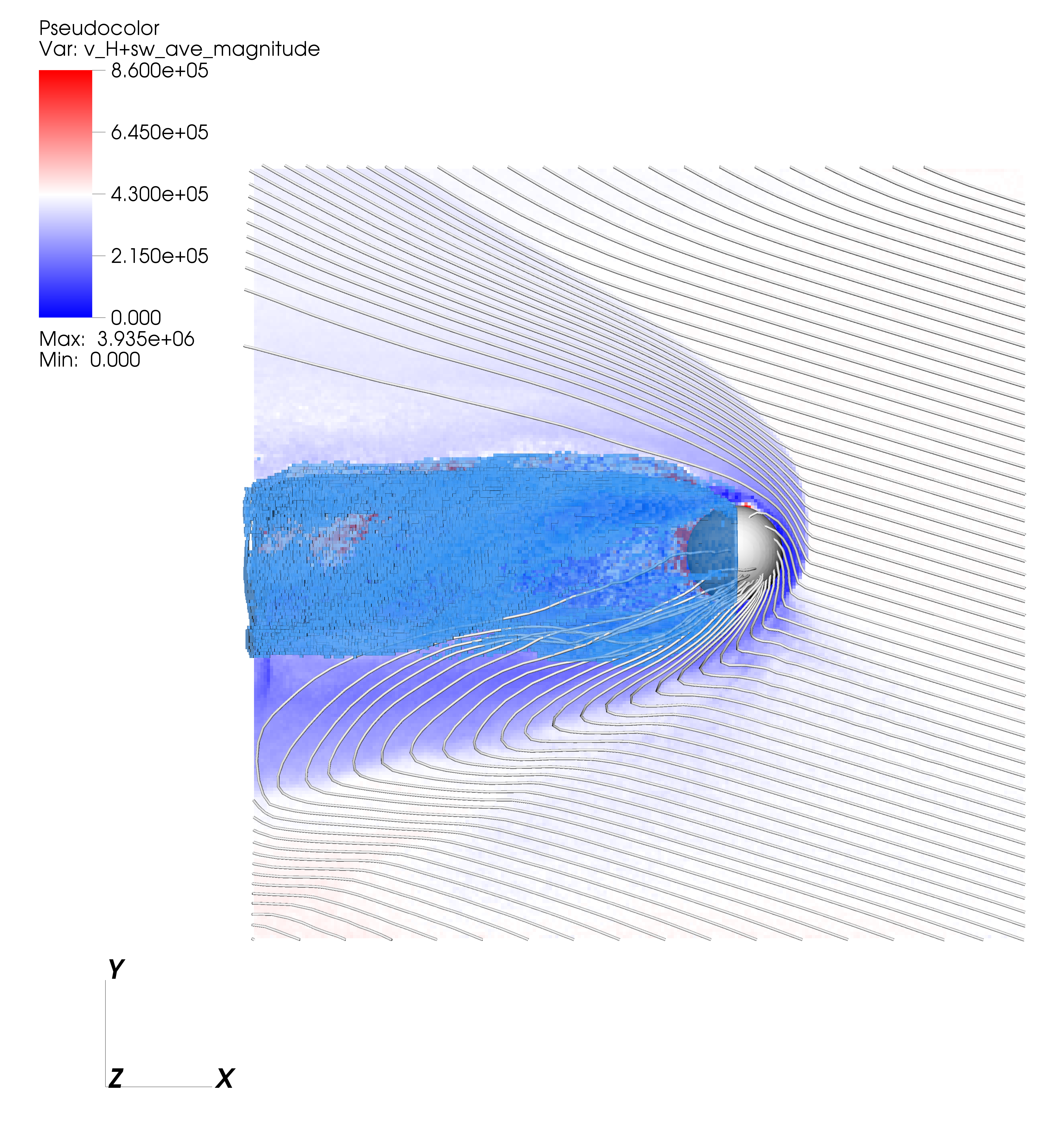
Moon's solar wind interaction
The solar wind interaction with the Moon in a global 3D RHybrid simulation run.
Young Moon's solar wind interaction
The solar wind interaction with young, magnetized Moon in a global 3D RHybrid simulation run.
Magnetic field draping at Venus
Draping of the interplanetary magnetic field lines around Venus and the formation of an induced magnetosphere in a global 3D RHybrid simulation run. (doi:10.1029/2020GL087462)
Ion escape from Venus
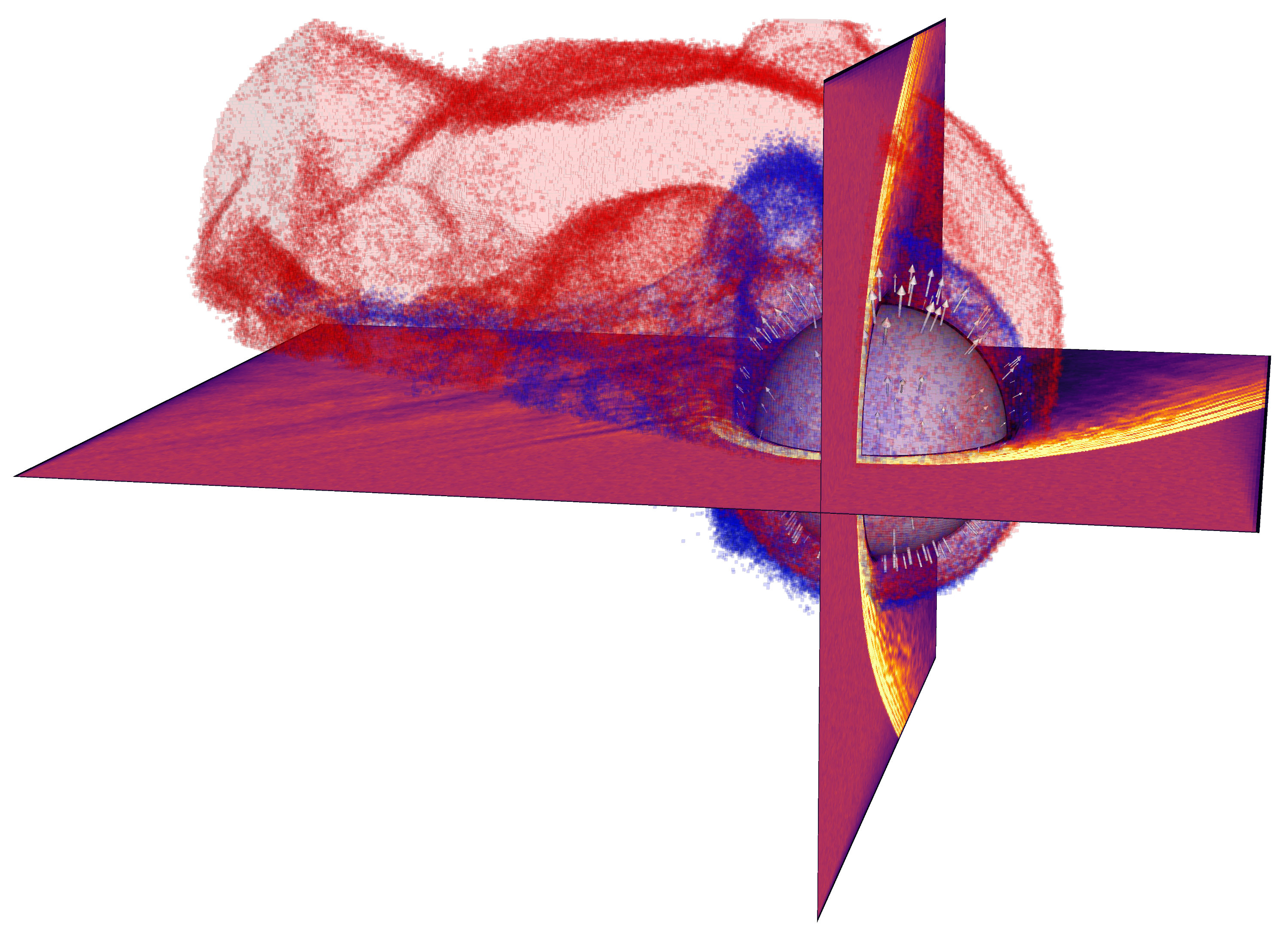
Solar wind driven escape of light (H+, blue) and heavy (O+, red) ions from Venus in a global 3D RHybrid simulation run. (doi:10.1029/2020GL087462)
BepiColombo Venus flyby (ion escape)
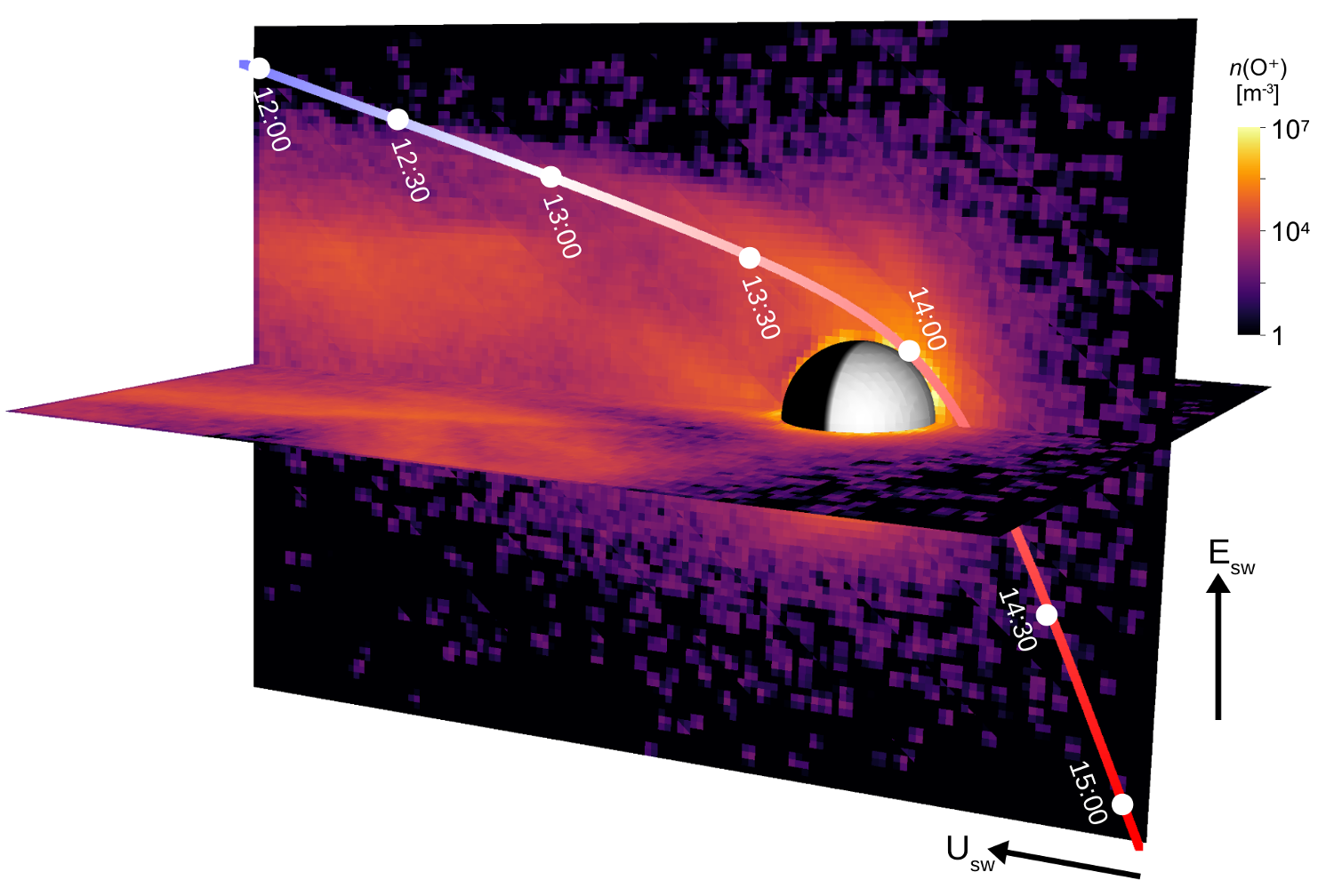
Global 3D RHybrid simulation of BepiColombo's Venus flyby and the density of escaping heavy oxygen ions.
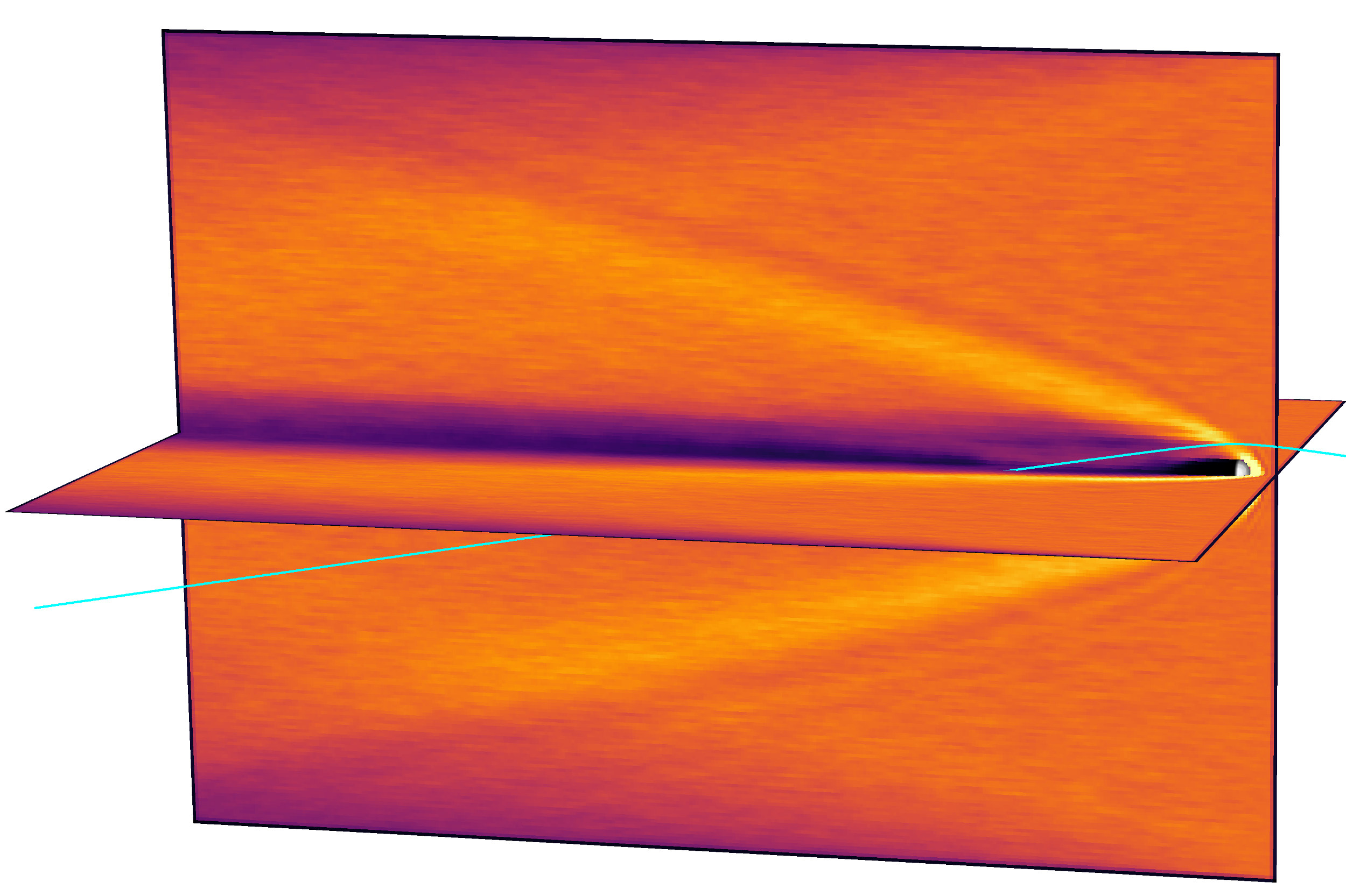
BepiColombo Venus flyby (solar wind)
Global 3D RHybrid simulation of BepiColombo's Venus flyby and the solar wind ion density.
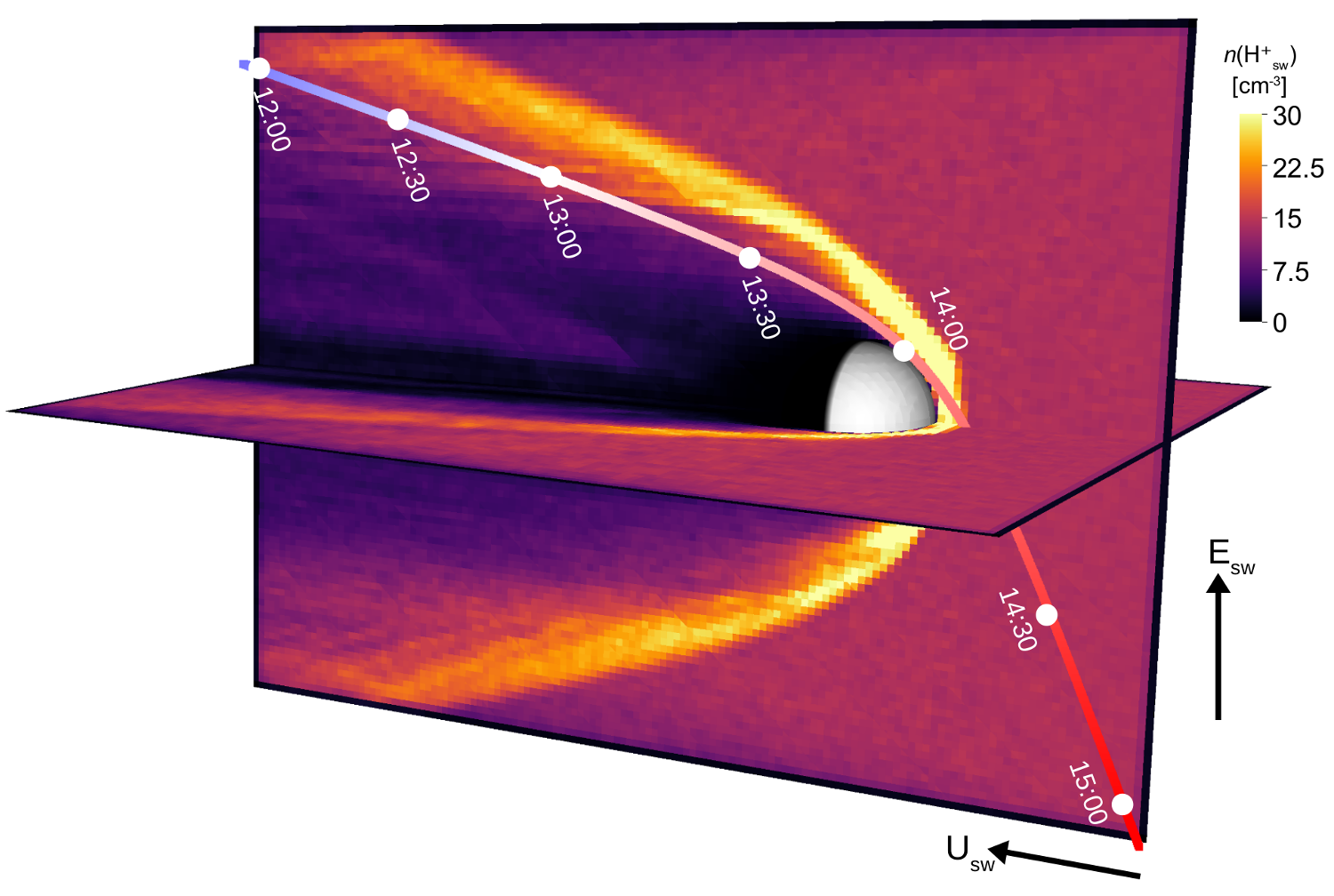
Solar Orbiter Venus flyby (solar wind)
Global 3D RHybrid simulation of Solar Orbiter's Venus flyby and the solar wind ion density.
Solar Orbiter Venus flyby (magnetic field)

Large-scale magnetic field draping and the formation of the Venusian induced magnetosphere in a global 3D RHybrid simulation of Solar Orbiter's Venus flyby.
Solar Orbiter Venus flyby (zoomed magnetic field)
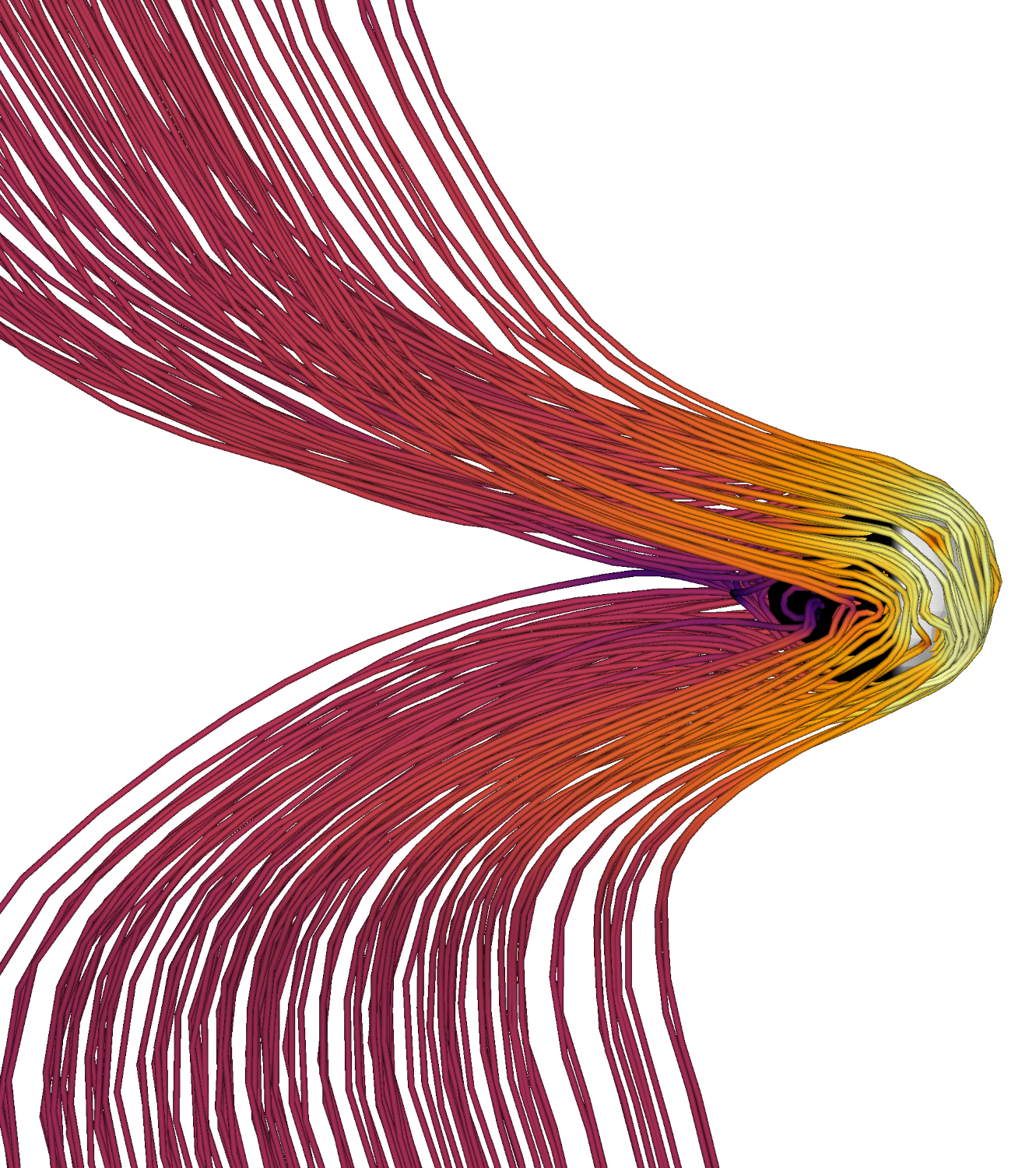

Near-planet magnetic field draping and the formation of the Venusian induced magnetosphere in a global 3D RHybrid simulation of Solar Orbiter's Venus flyby.
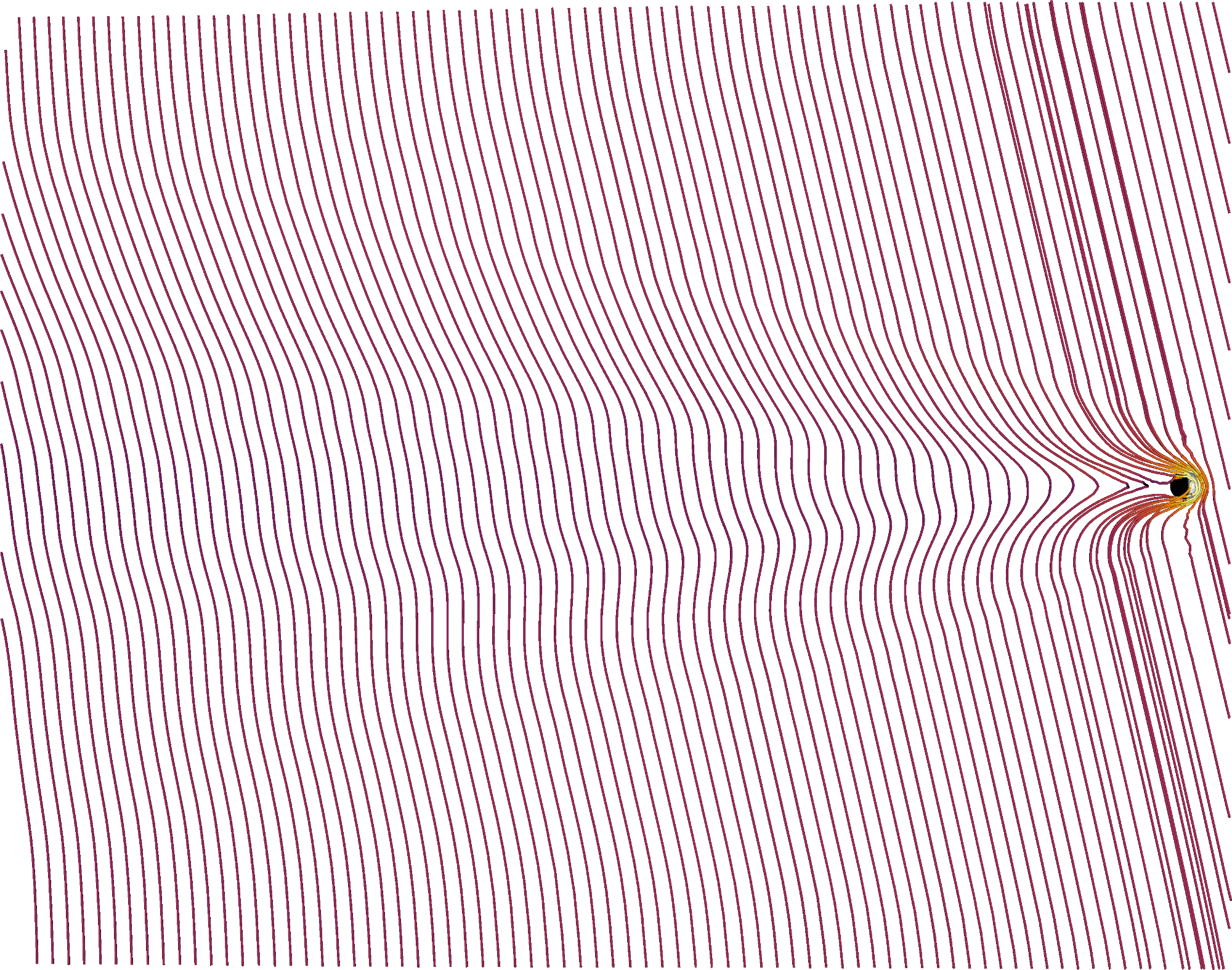
Foreshocks of terrestrial planets
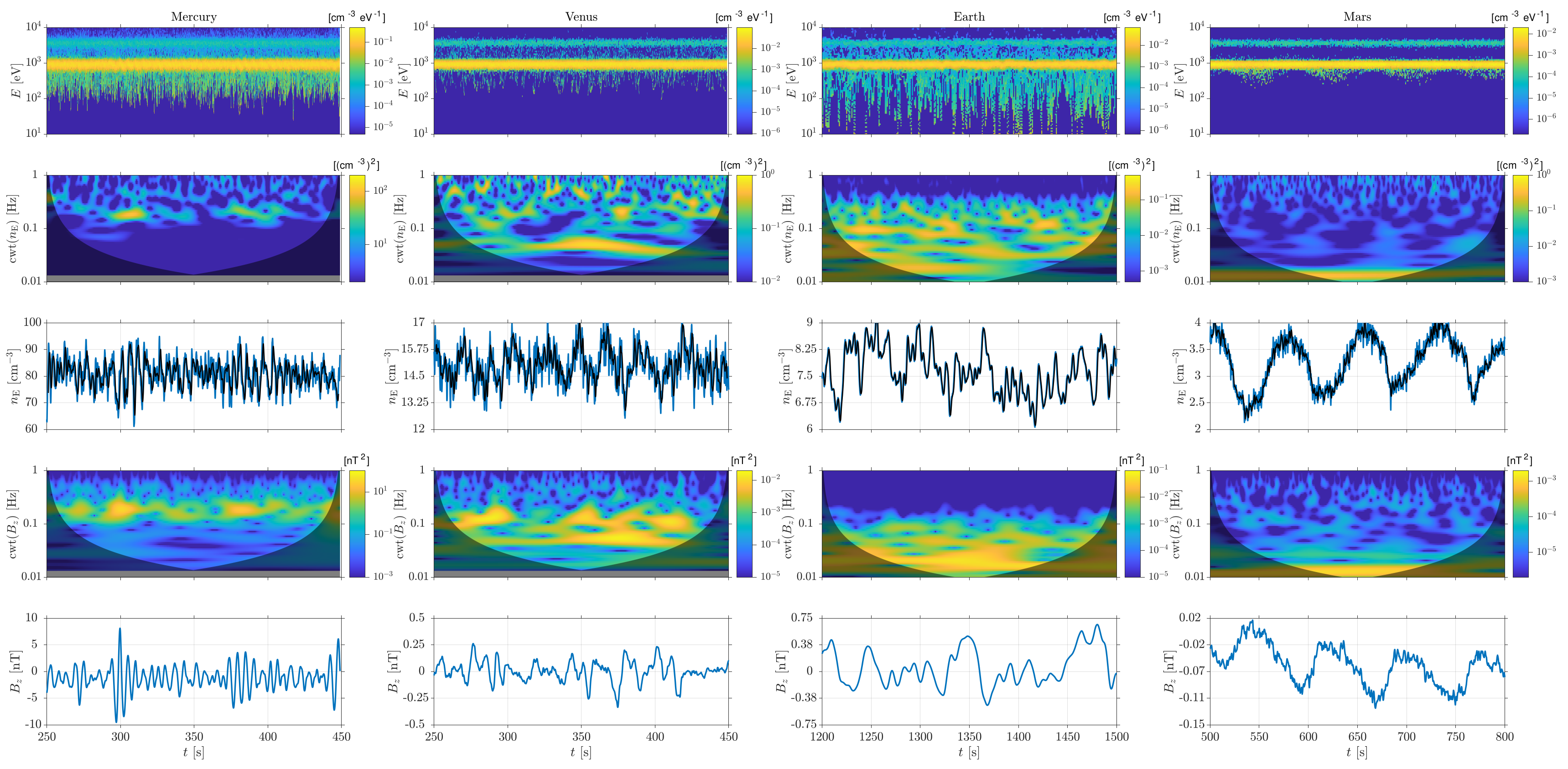
Virtual spacecraft time series extracted from global 3D RHybrid simulation runs of the ion foreshock formation at solar system's terrestrial planets.
Foreshocks of terrestrial planets (ion distributions)
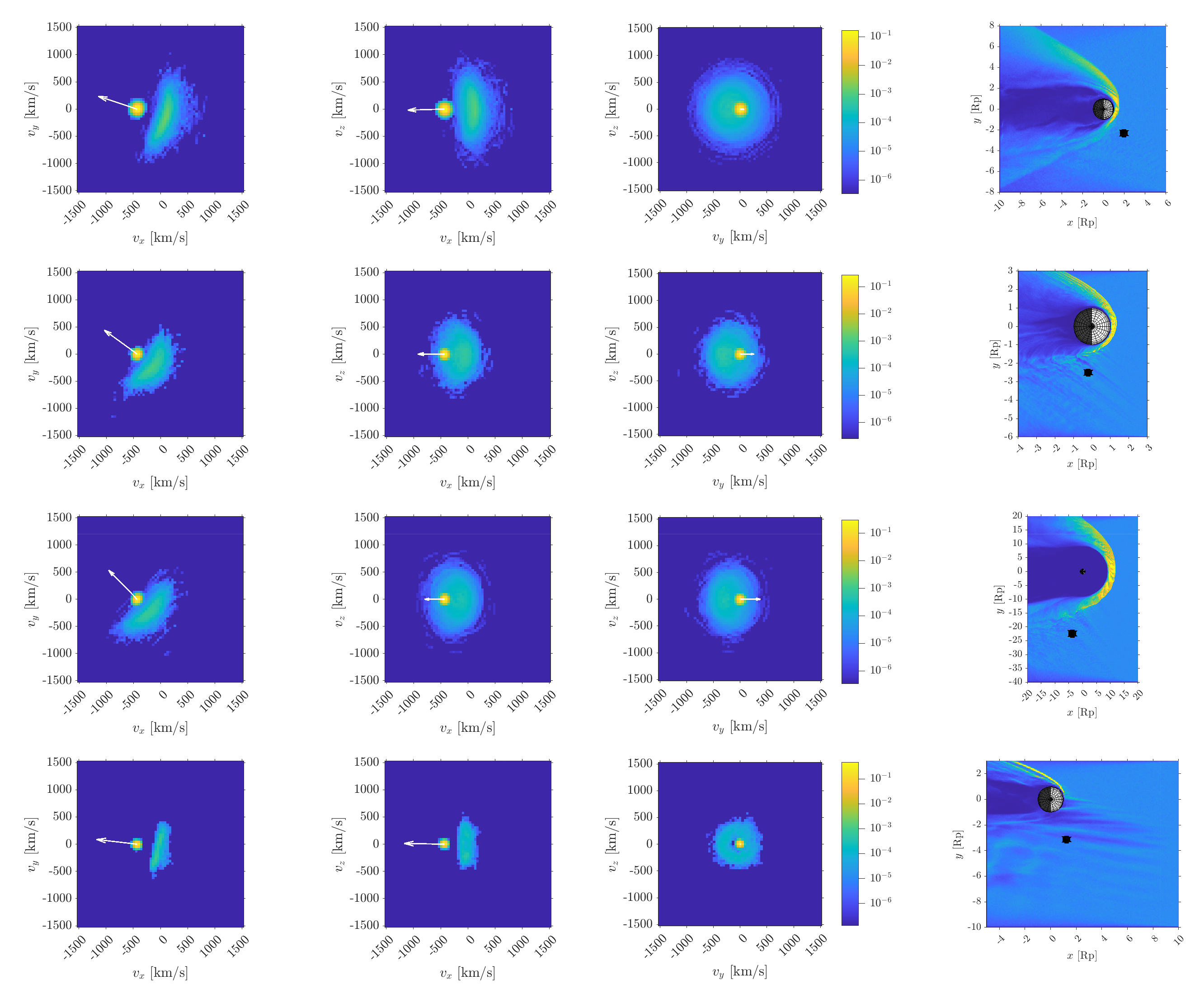
Solar wind ion velocity distributions extracted from global 3D RHybrid simulation runs of the ion foreshock formation at solar system's terrestrial planets.
Field-aligned currents at Mercury
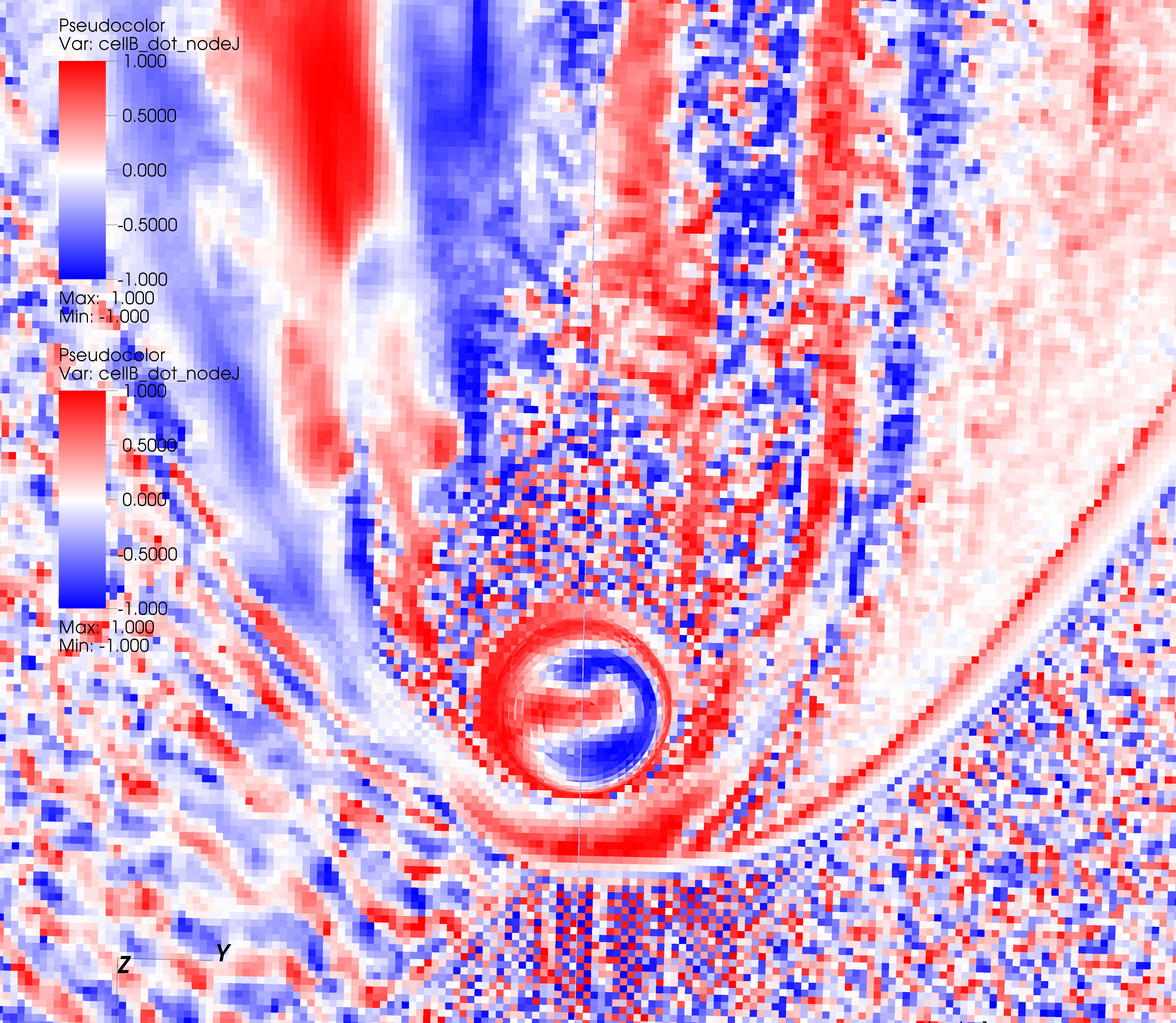
Electric current aligned (red) and anti-aligned (blue) with magnetic field in the Hermean magnetosphere.
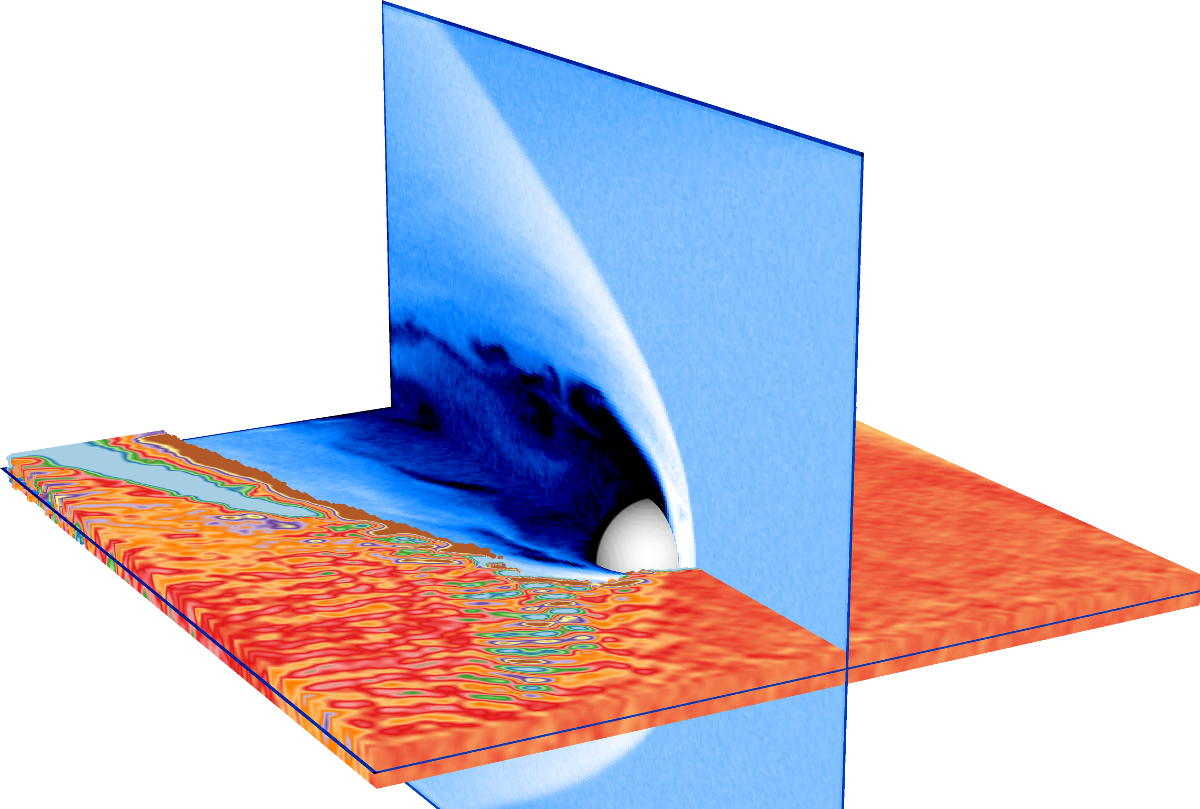
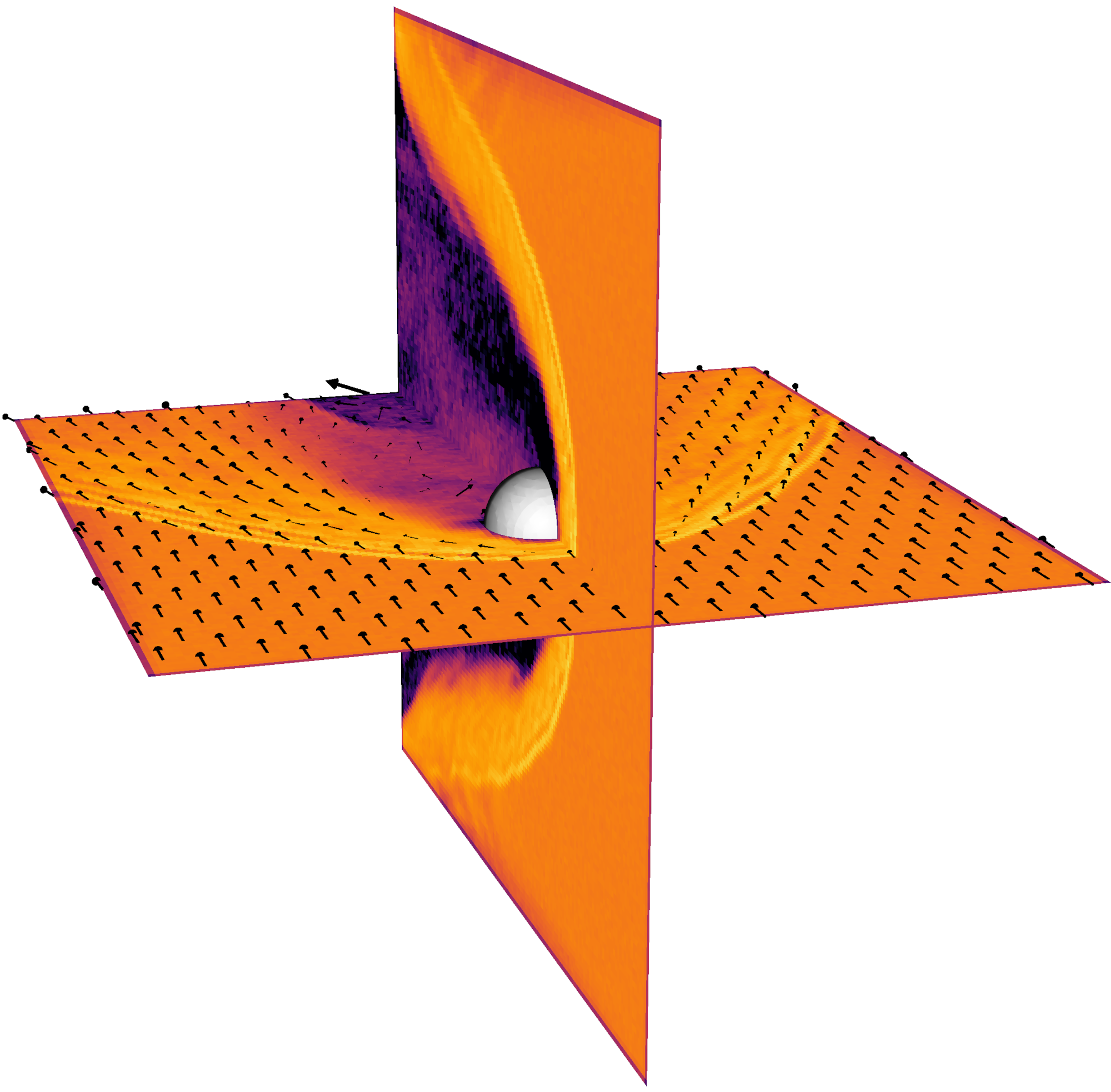
Dayside hemispheric asymmetry
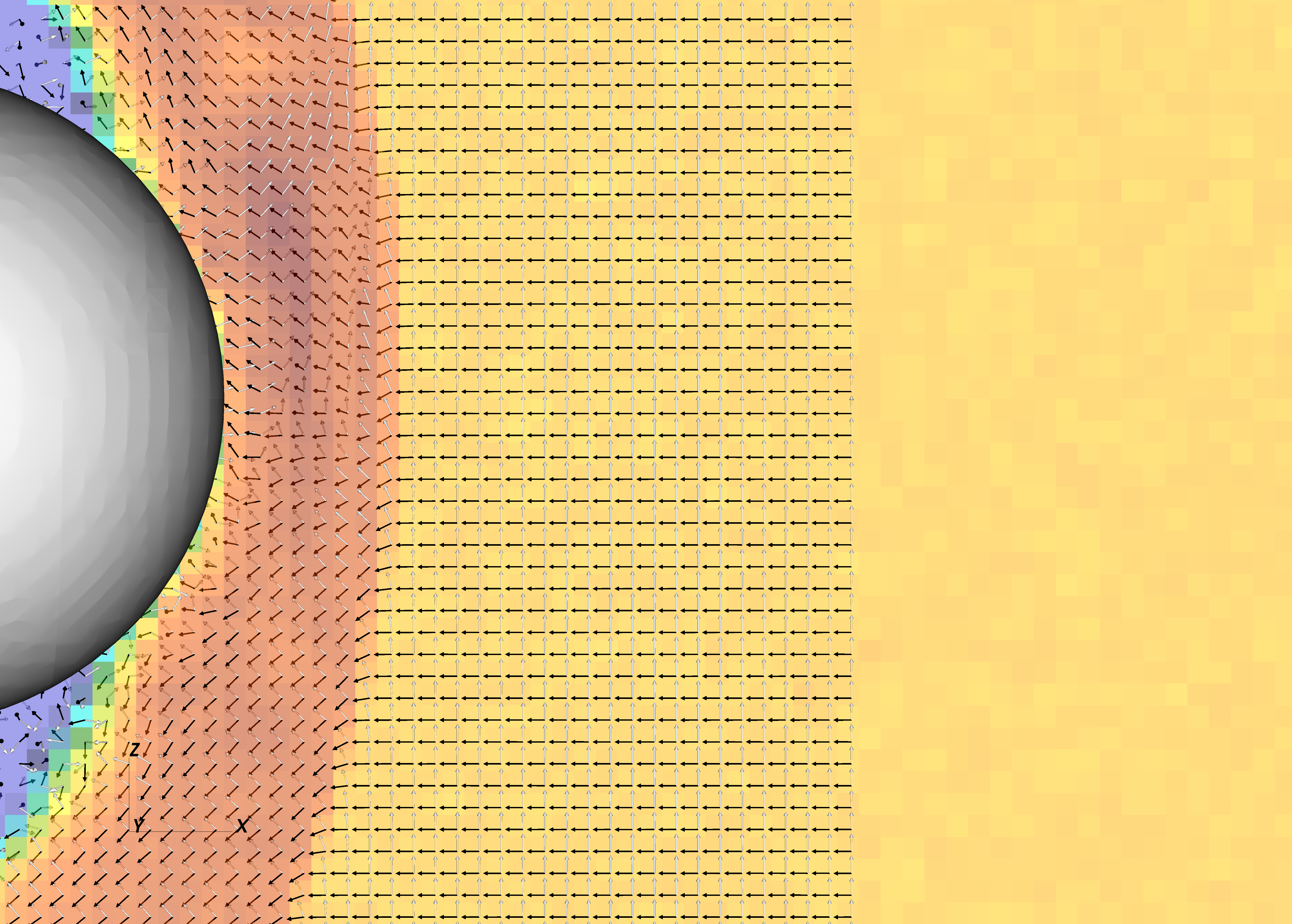
The formation of initial dayside hemispheric asymmetry due to Hall and kinetic ion effects in an induced magnetosphere in the global 3D RHybrid simulation. Black vectors are the plasma bulk velocity and white vectors are the electric field.
ULF foreshock waves at Earth
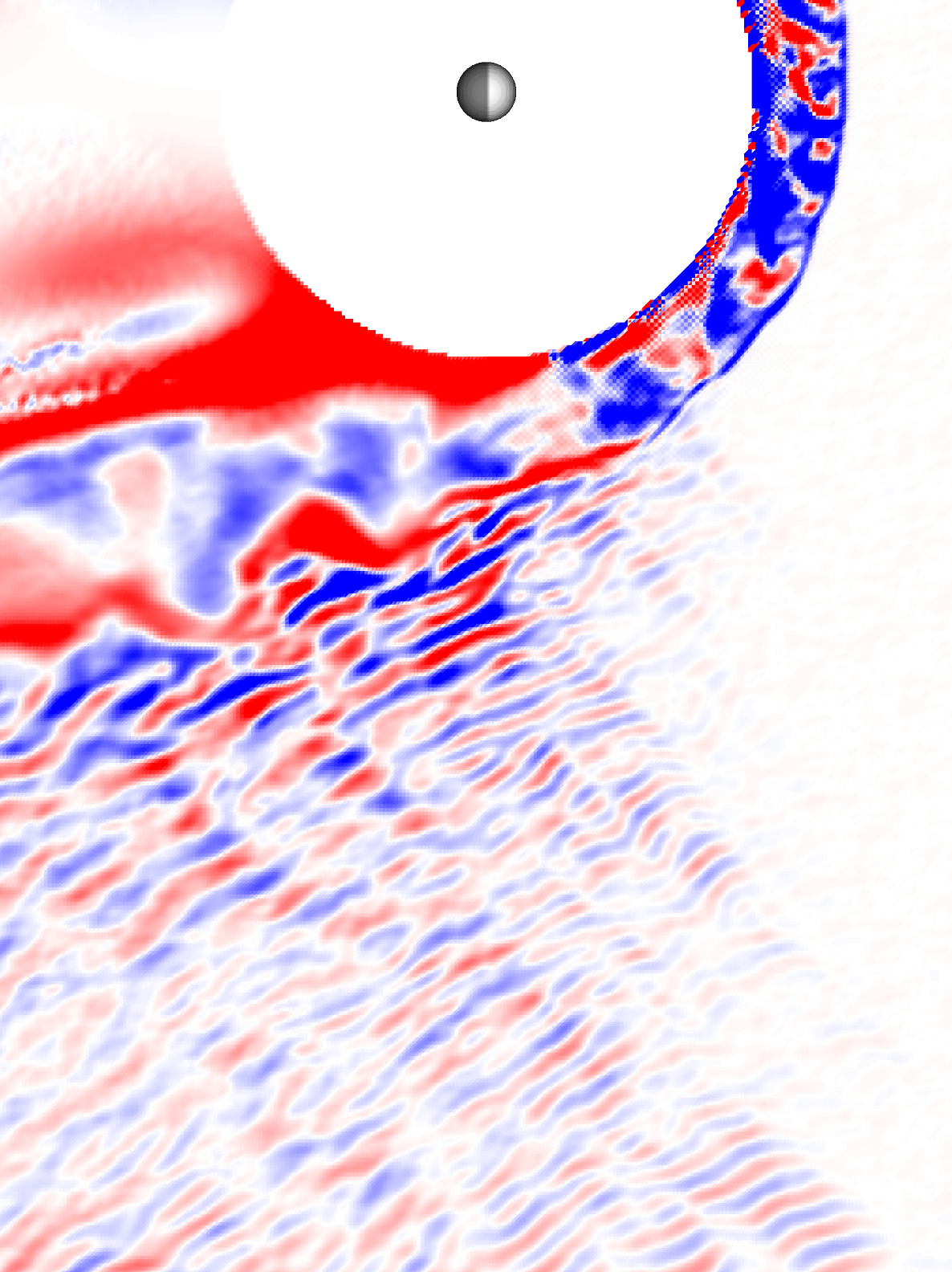
The formation of the ion foreshock and the ULF waves ahead of the quasi-parallel bow shock near Earth in the global 3D RHybrid simulation.
Carbon escape from young Mars
Solar wind driven escape of carbon ions from young Mars at 10 times the present day EUV flux. (doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2022.115009)
Oxygen escape from young Mars
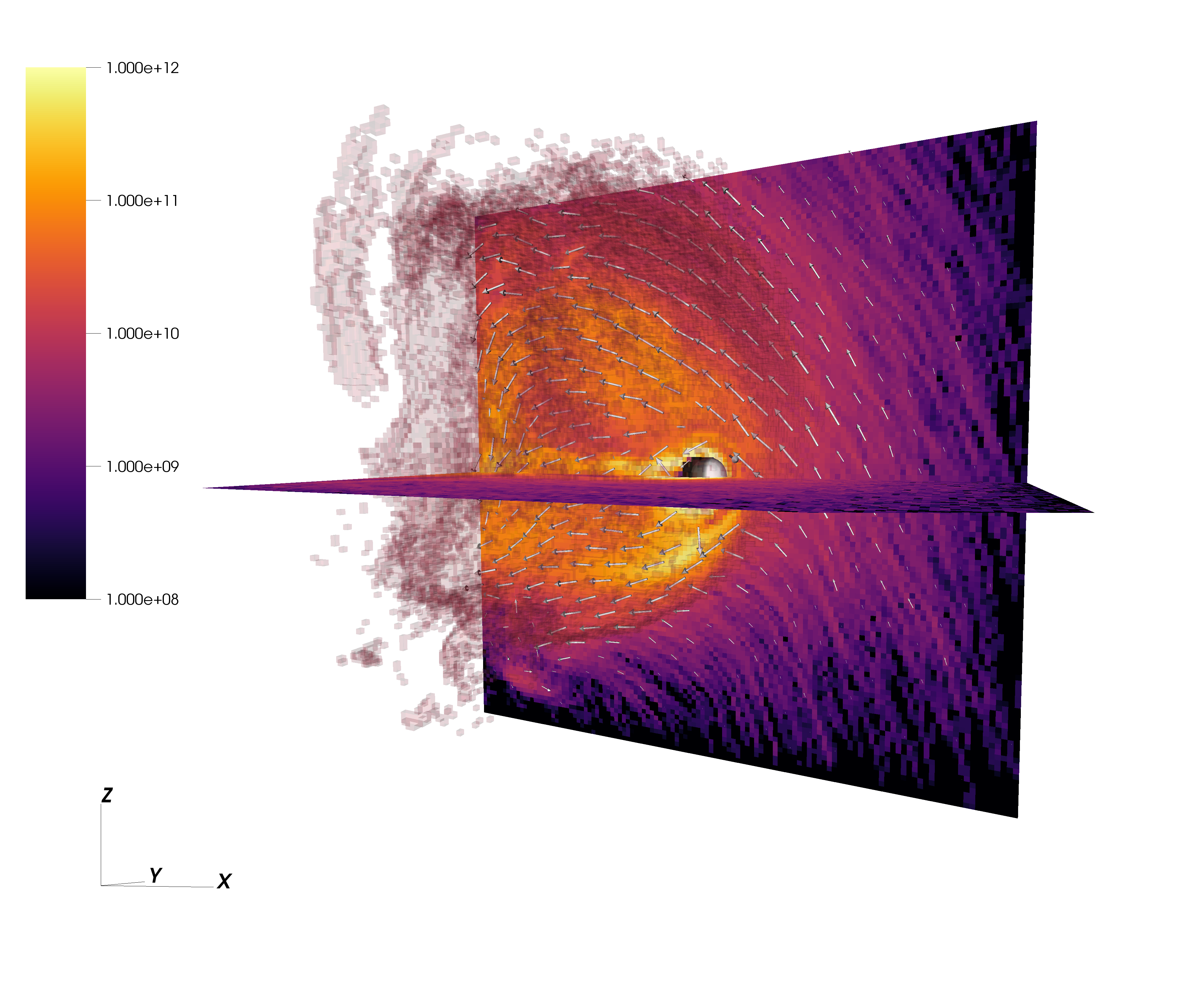
Solar wind driven escape of oxygen ions from young Mars at 10 times the present day EUV flux. (doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2022.115009)
Solar wind interaction with young Mars
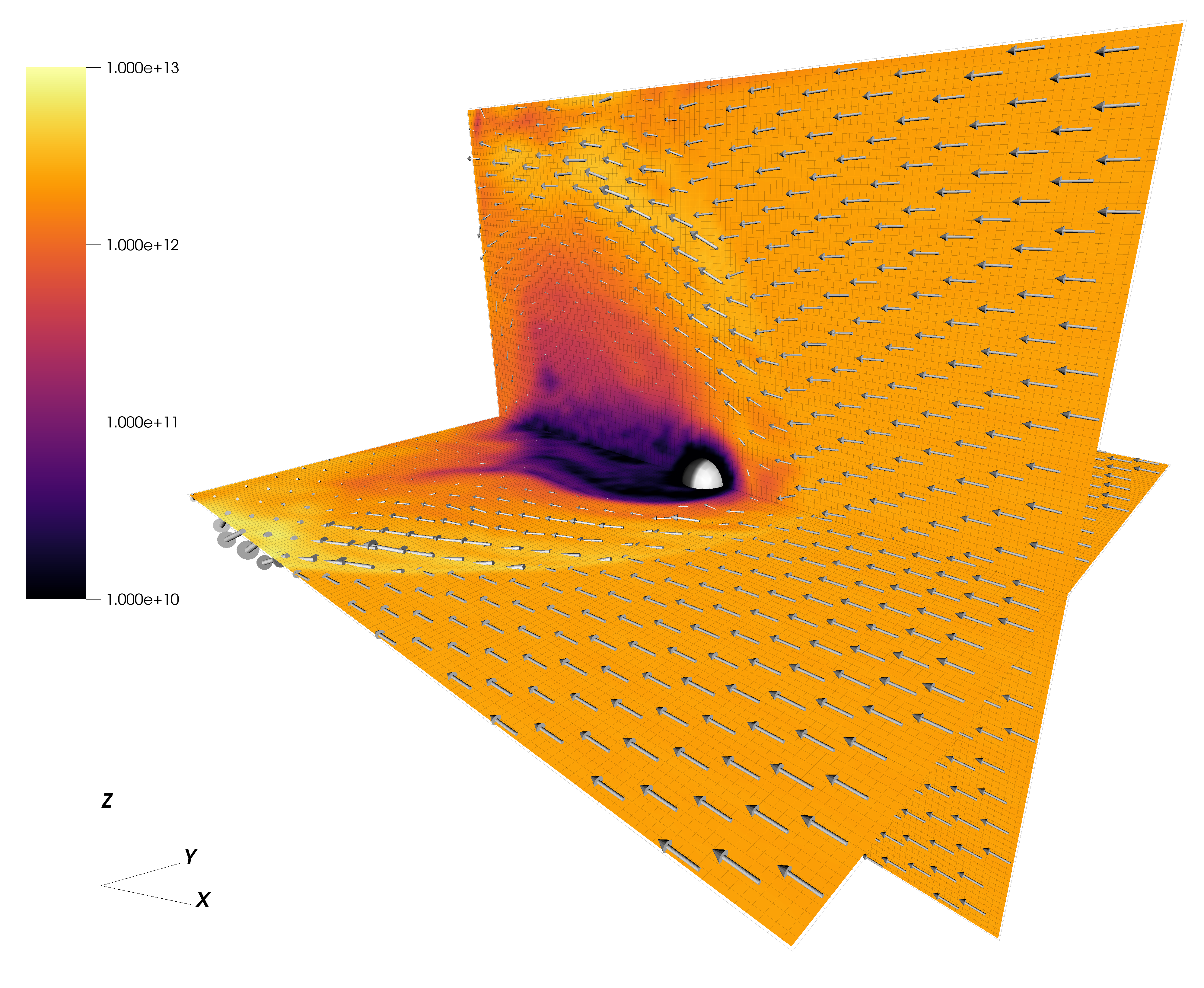
Solar wind interaction and an induced magntosphere of young Mars at 10 times the present day EUV flux. (doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2022.115009)
Oxygen ion escape from Mars
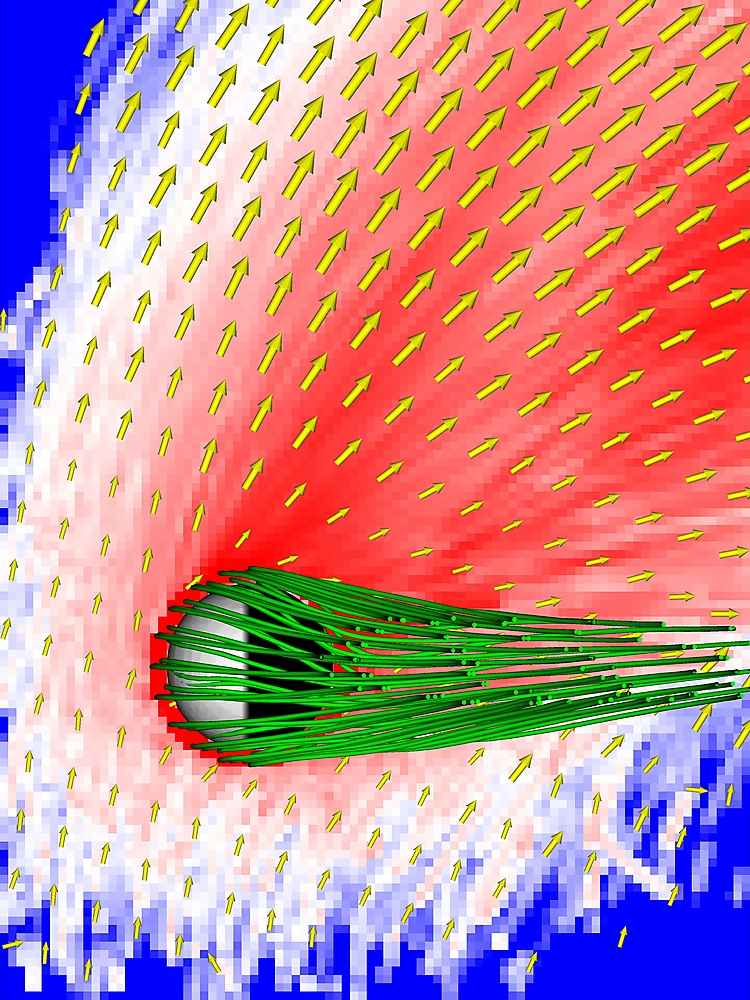
Solar wind driven oxygen ion escape from Mars under perpendicular interplanetary magnetic field to the upstream solar wind flow. Green field lines show the magnetic field draping around Mars. Upstream solar wind convection electric field points upwards in the figure.
Oxygen ion escape from magnetized Mars (dipole)
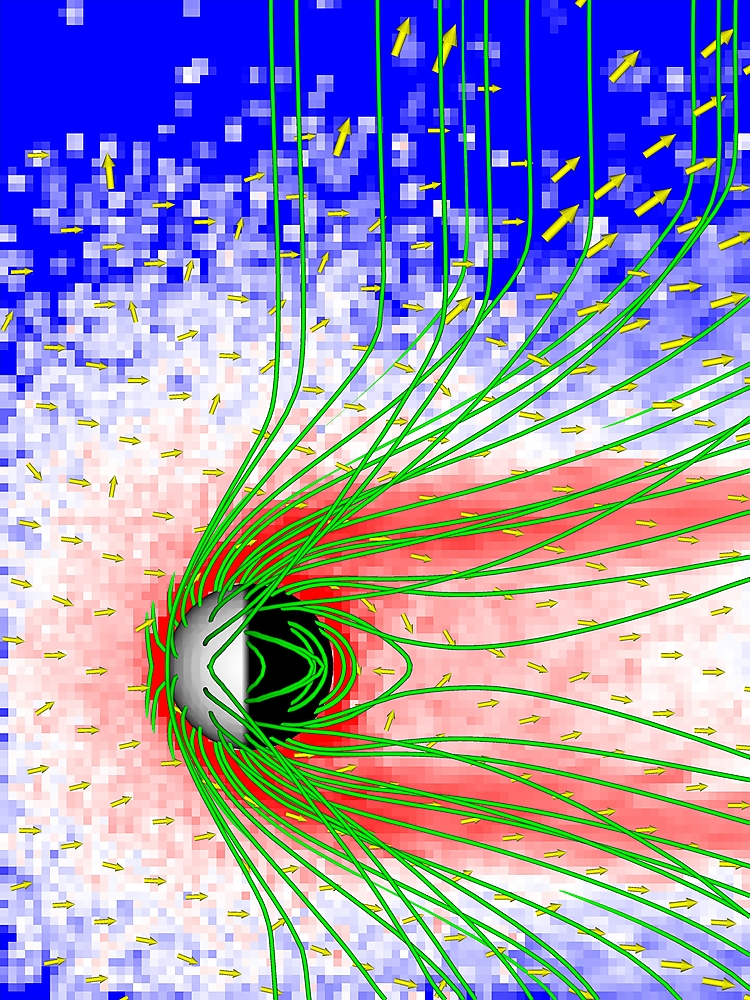
Solar wind driven oxygen ion escape from young Mars with a global magnetic dipole field.
Oxygen ion escape from magnetized Mars (hemispheric dipole)
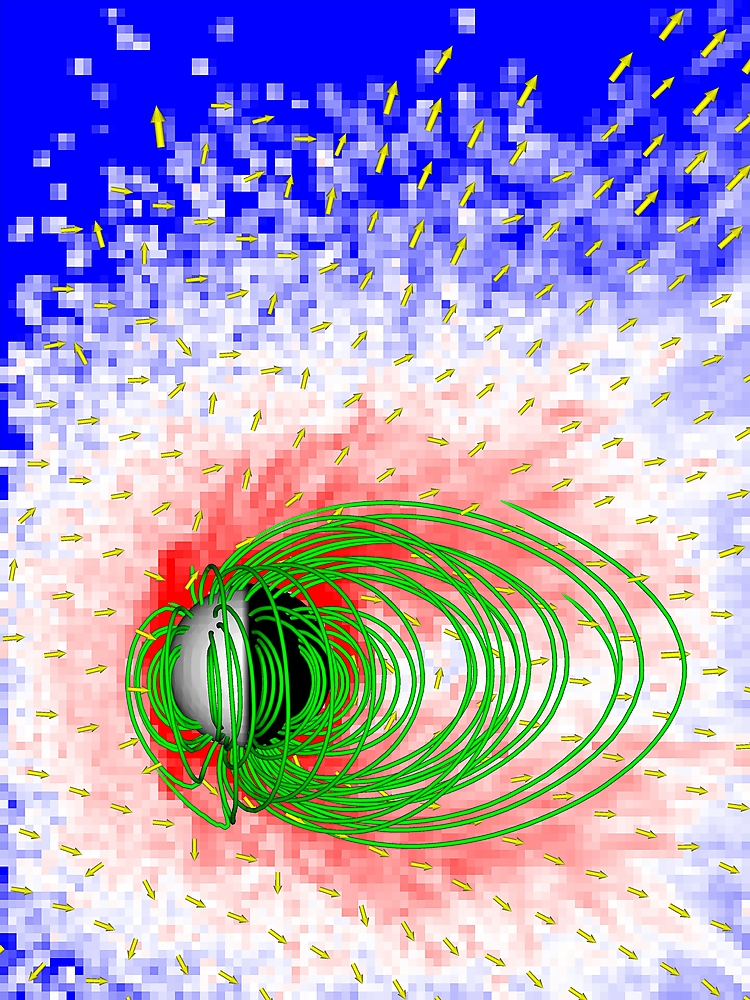
Solar wind driven oxygen ion escape from young Mars with a global hemispherically asymmetric magnetic dipole field.
Mars with hemispheric dipole field
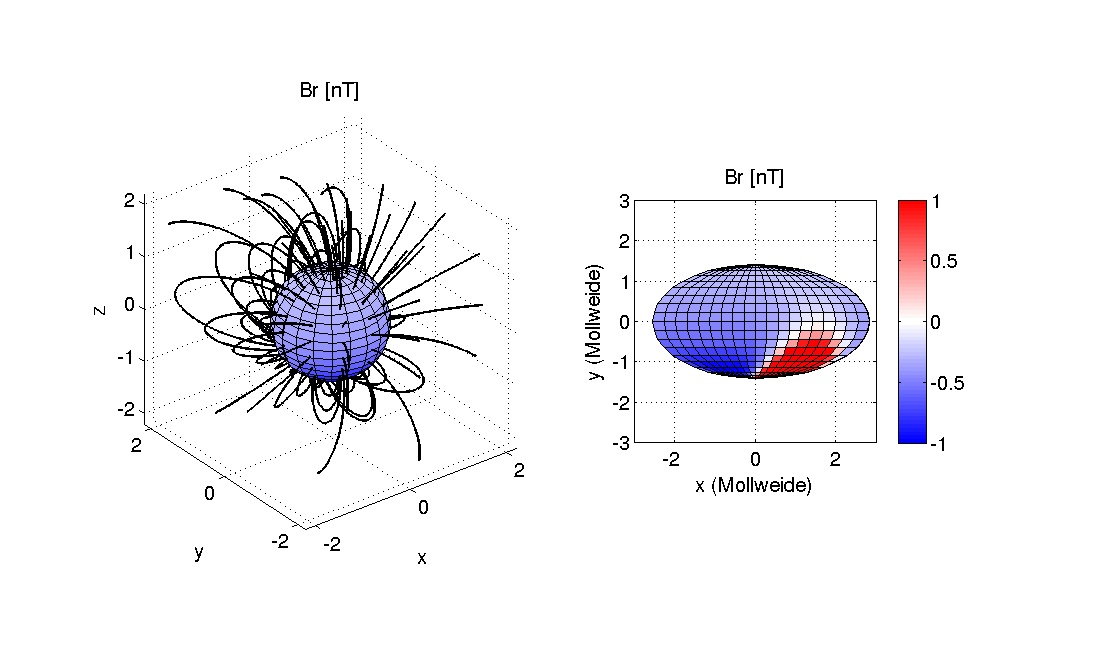
Young Mars with a hemispherically asymmetric global dynamo field.
Solar wind interaction with a lunar magnetic anomaly
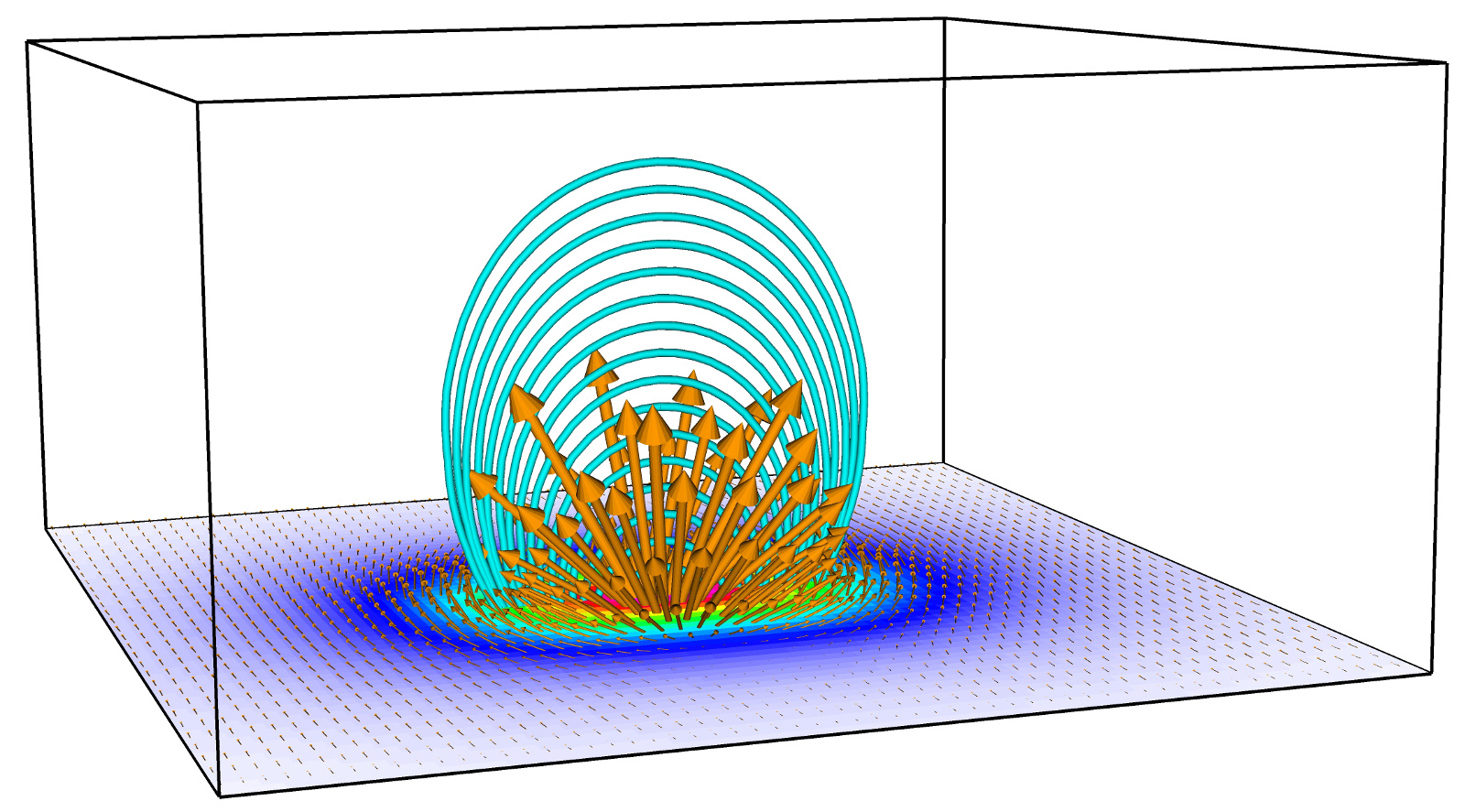
Solar wind interaction with a lunar crustal magnetic anomaly near the Gerasimovich crater in the HYB simulation. The simulation domain covers 200 km in altitude and 400 km x 400 km perpendicular area. Orange vectors show the antimoonward electric field.
Hybrid simulation of 3D shock
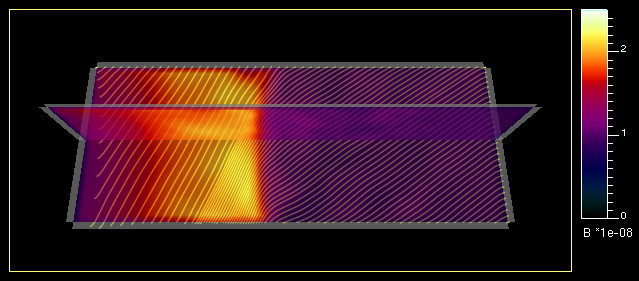
The HYB simulation model run of a 3D dimensional, collision-less plasma shock.
Flying along Venus Express orbit
3D models can be used to obtain insights and give global context about regions through which spacecraft travel and make local observations. In the video the viewpoint is moving along a true orbit of ESA's Venus Express spacecraft in the Venus plasma environment (doi:10.5194/angeo-27-4333-2009,10.1002/jgra.50387).
Flying in the induced magnetosphere of Titan
Saturn moon Titan's interaction with the co-rotating plasma in the Kronian magnetosphere. Surface encompasses areas of highest magnetic flux. Orbital plane is shown with colors indicating magnetic flux values. Field lines show the draping of the magnetic field around Titan's ionosphere. (doi:10.1029/2011JA016443)
Ion time-energy spectrogram
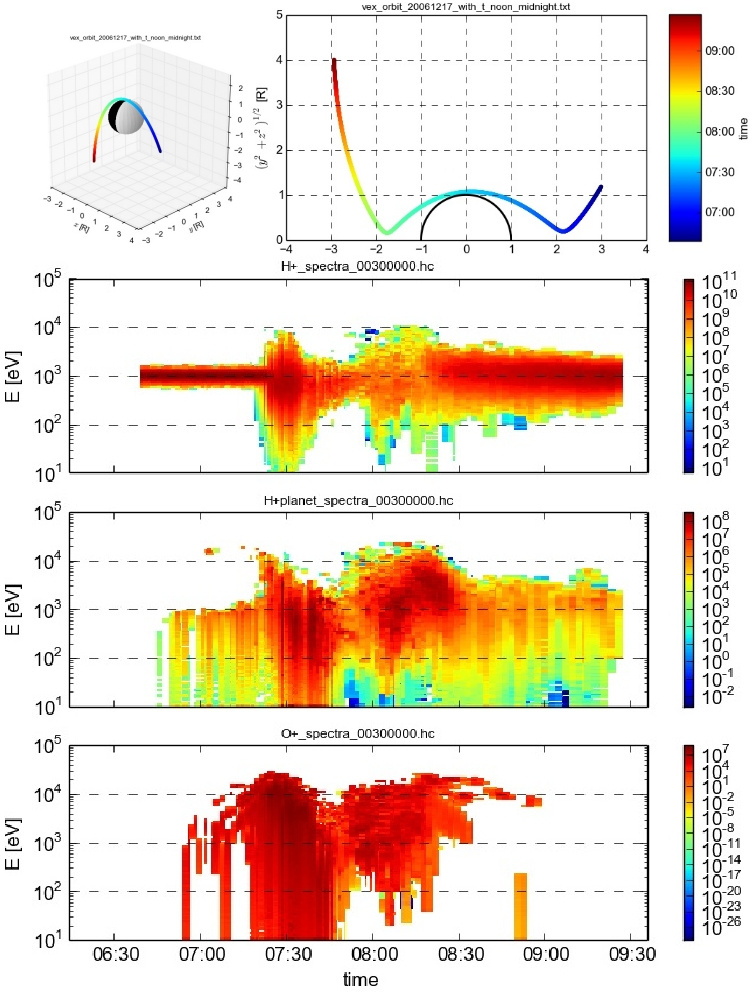
Ion time-energy spectrograms of H+ (solar wind), H+ (planetary) and O+ (planetary) ions along the Venus Express trajectory.
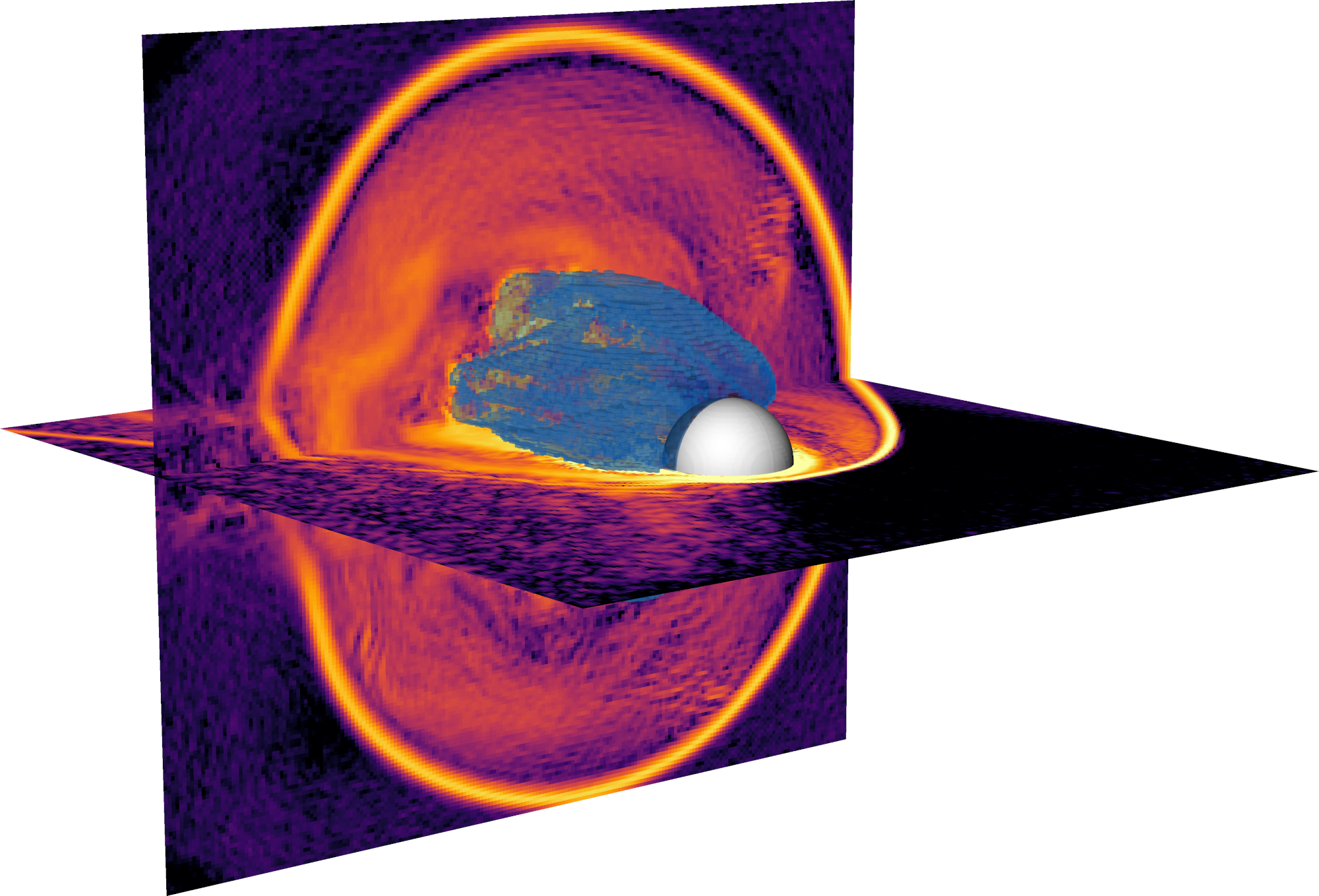
Heavy ion escape from Mars
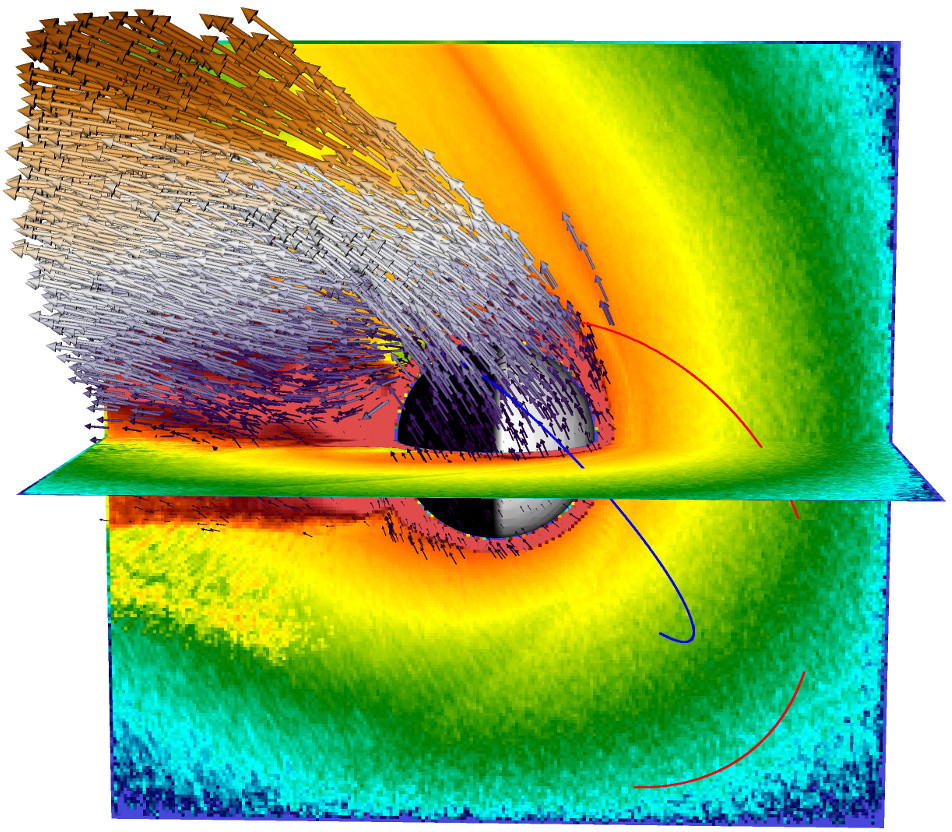
High resolution parallel modeling of the solar wind driven ion erosion from Mars. Sources of the Mars ions are the almost spherically symmetric exosphere and the ionosphere. (doi:10.1002/2017JA024884)
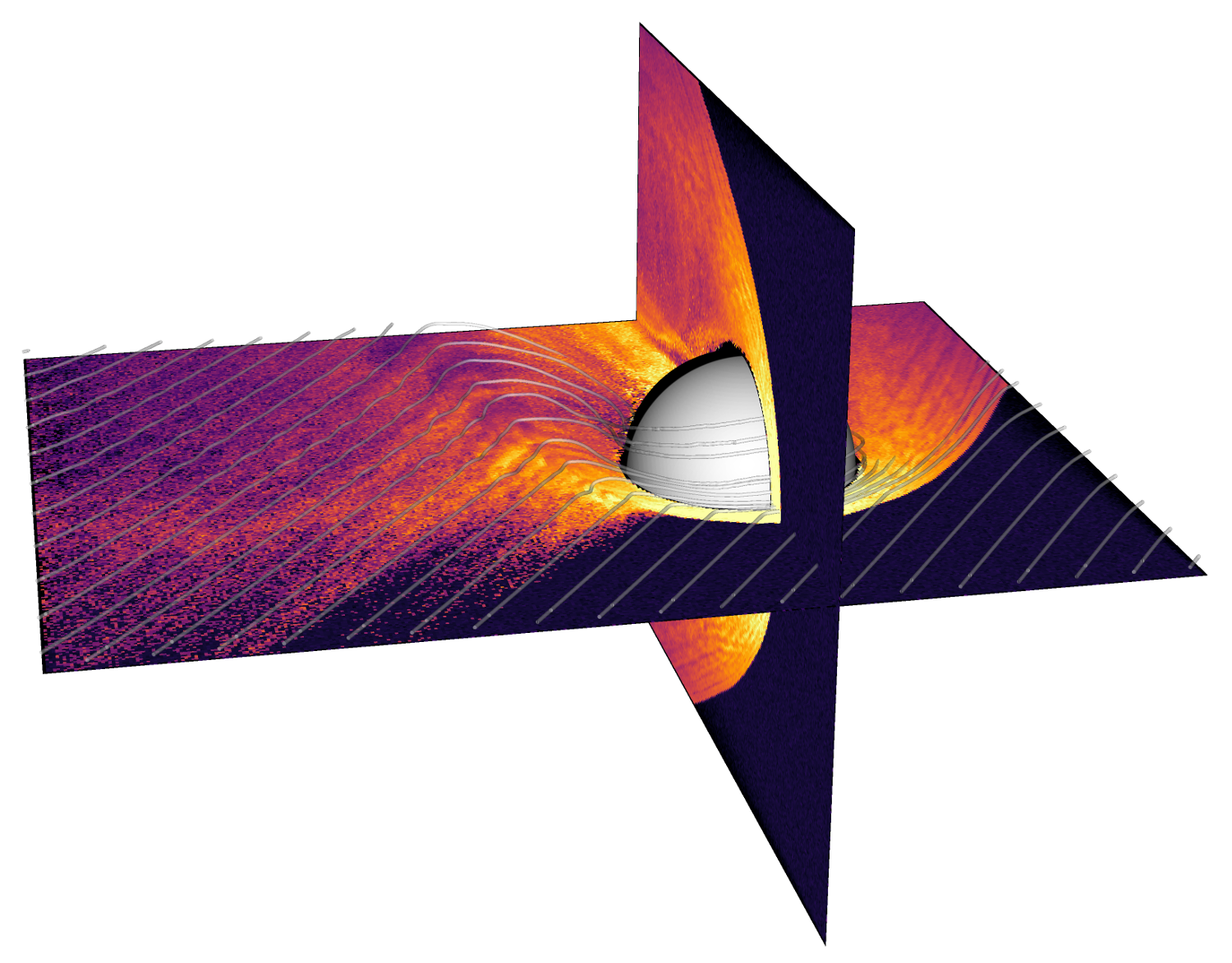
ULF waves and ion escape from Mars
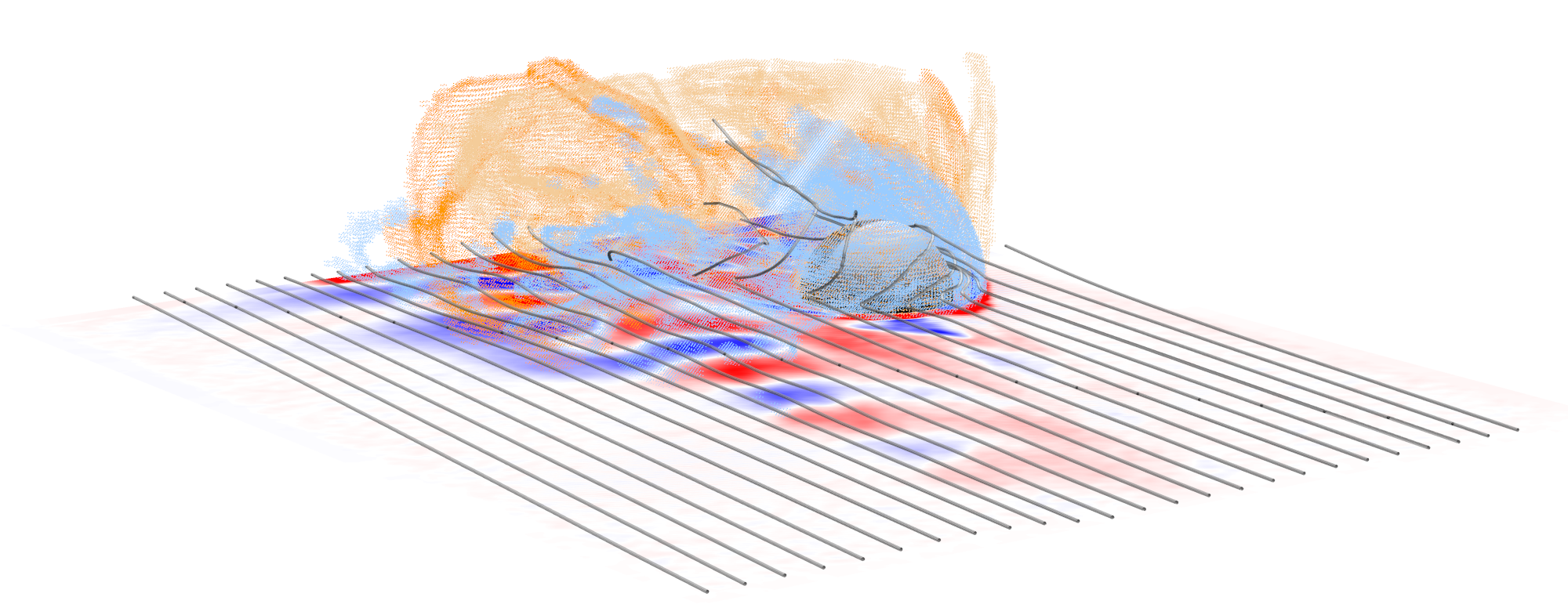
A global 3D RHybrid simulation run of the solar wind interaction with Mars and the resulting planetary ion escape (light blue and yellow regions) and its coupling with the foreshock ULF waves (blue-red) under radial interplanetary magnetic field conditions. (doi:10.1029/2021JA030078)
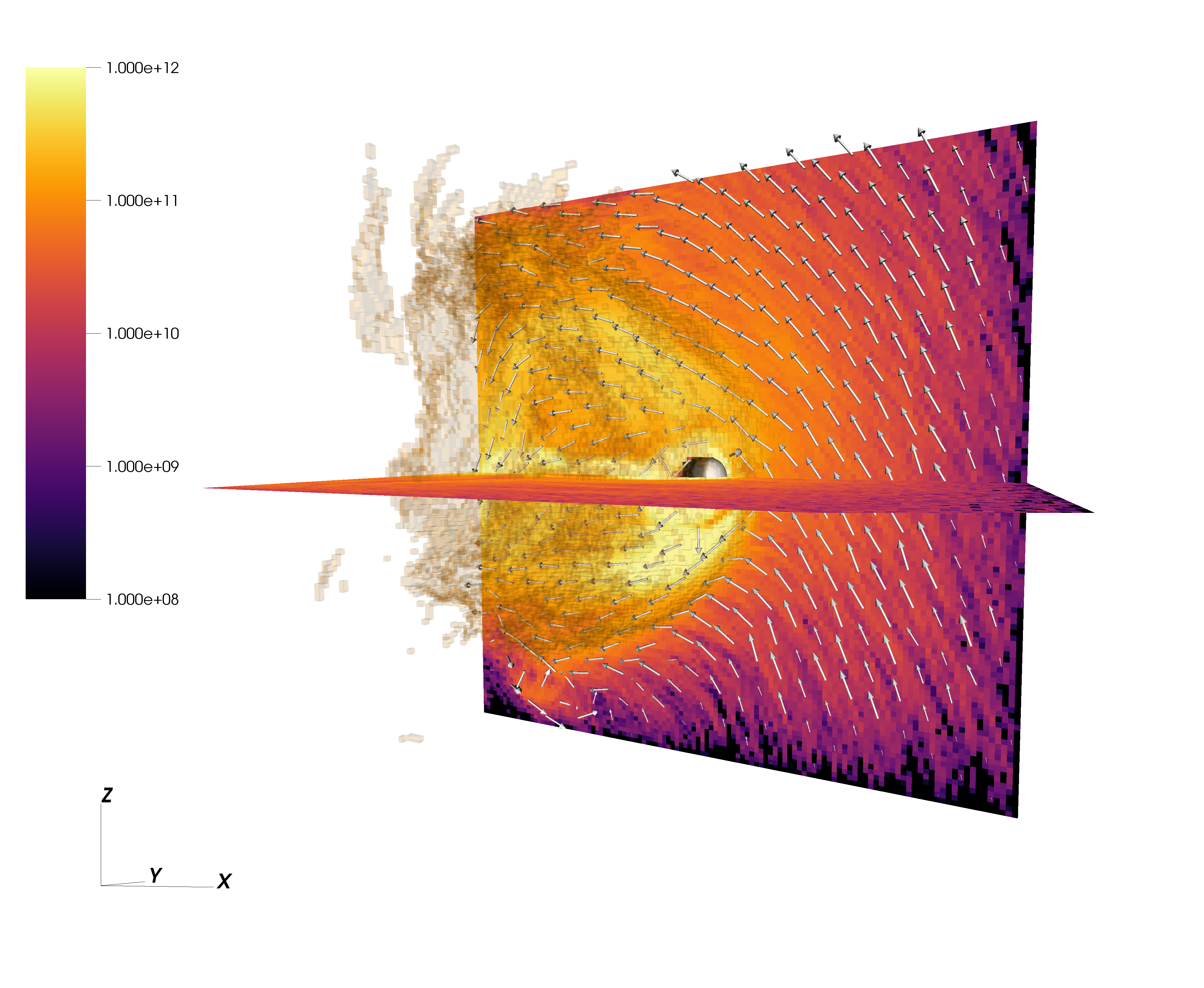
Induced magnetosphere of Mars
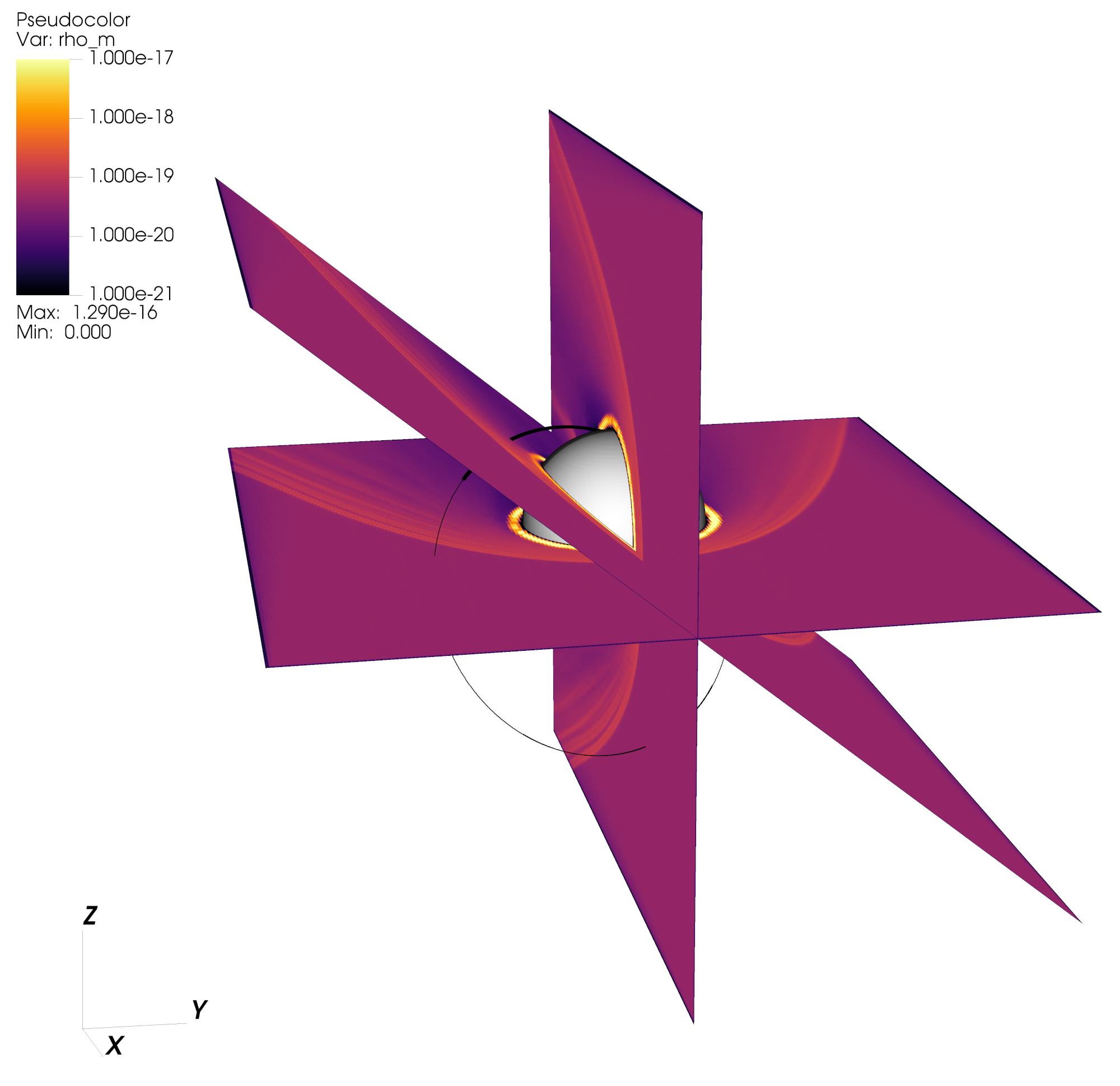
Total ion mass density in the induced magnetosphere of Mars and the MAVEN orbit trace in the RHybrid simulation domain.
Solar storm at Venus
Time dependent phenomena in planetary plasma environments. Video illustrates how the Venus plasma environment is disturbed when it is hit by a space weather disturbance travelling from the Sun. In the simulation the disturbance is a short duration density enhancement in the solar wind. Note how the disturbance "shakes" the whole plasma environment of Venus, triggering in its wake instabilities and turbulence in the plasma, which after some time returns back to an equilibrium state.
Atmospheric erosion at Venus
A three dimensional (3D) view of the plasma physical processes at unmagnetized planets and other celestial bodies. Video illustrates how the density of atomic oxygen ions (O+) escaping from Venus would look like at different positions around Venus.
Induced magnetosphere of Titan
Titan's interaction with the co-rotating plasma in the magnetosphere of Saturn. Surface encompasses areas of highest magnetic flux. Orbital plane is shown with colors indicating magnetic flux values. Field lines show the draping of the magnetic field around Titan's ionosphere. (doi:10.1029/2011JA016443)
Escaping elements of water at Venus
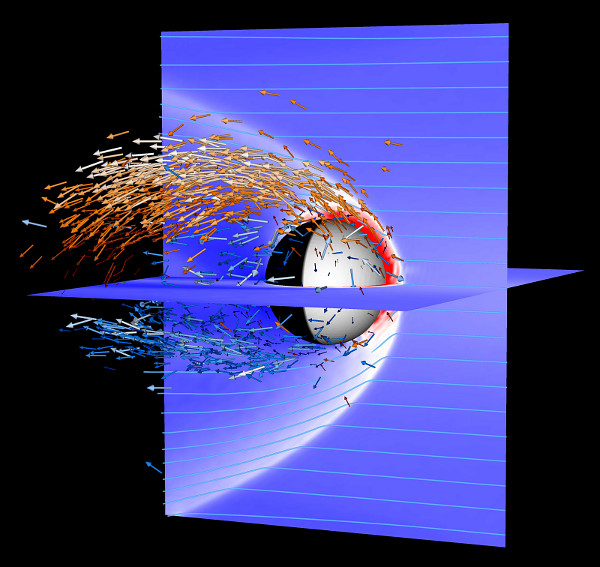
Solar wind driven oxygen (orange arrows) and hydrogen (blue arrows) ion escape from Venus. (doi:10.1029/2010GL044062)
Induced magnetosphere of Venus
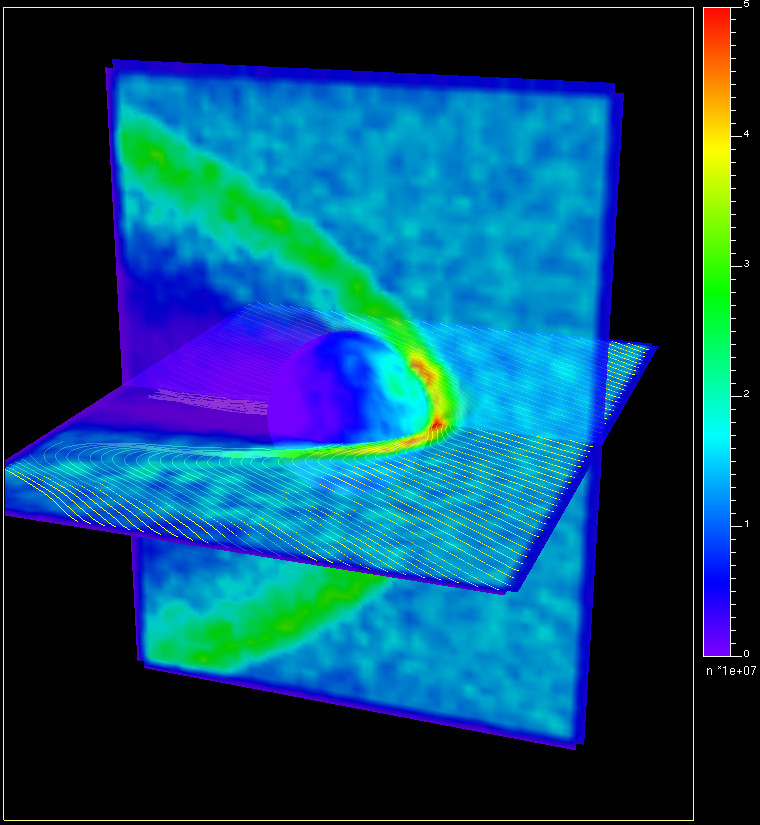
Density of the solar wind protons in the Venusian induced magnetosphere (color coding) showning the bow shock (red-green) and the low density wake and magnetotail of the planet (magenta-blue). Yellow lines illustrate the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) draping around Venus.
Current system in the Venus magnetotail
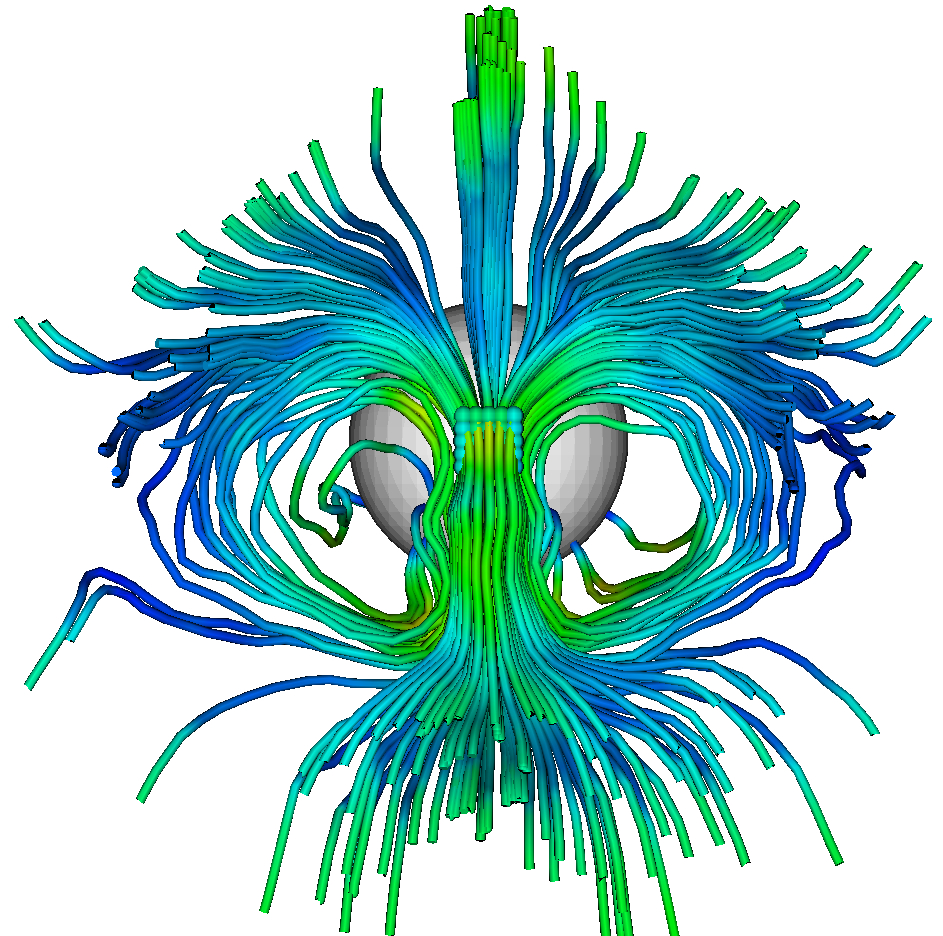
Estimation of the electric current system in the induced magnetotail of Venus. The central tail current sheet (CTCS) points from down to top in the center of the figure and circles symmetrically around the two magnetic lobes of the tail. (doi:10.1002/jgra.50387)
Formation of the ionized gas tail of a comet
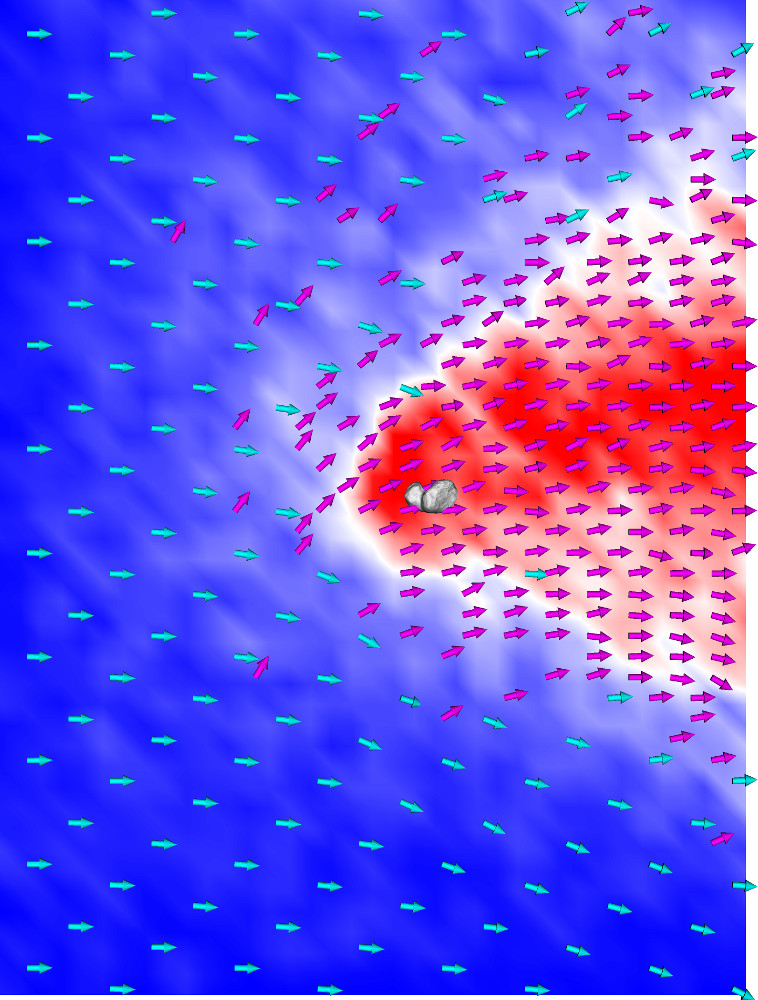
Large scale interaction of a comet and the solar wind, which leads to the formation of the cometary ionized gas tail.
Magnetosphere of Mercury
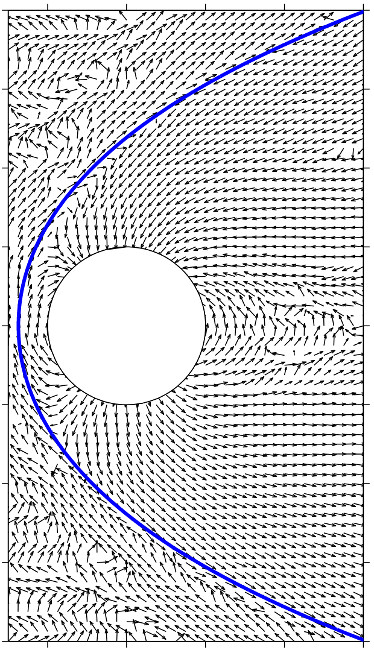
Magnetic field vectors and the bow shock at Mercury. (doi:10.5194/angeo-21-2133-2003)
Magnetic morphology near Venus
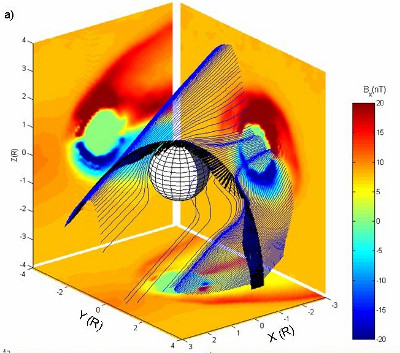
Magnetic field line tracing in the Venus induced magnetosphere using the HYB model along the Venus Express orbit. (doi:10.1016/j.pss.2007.09.011)
Leapfrog algorithm
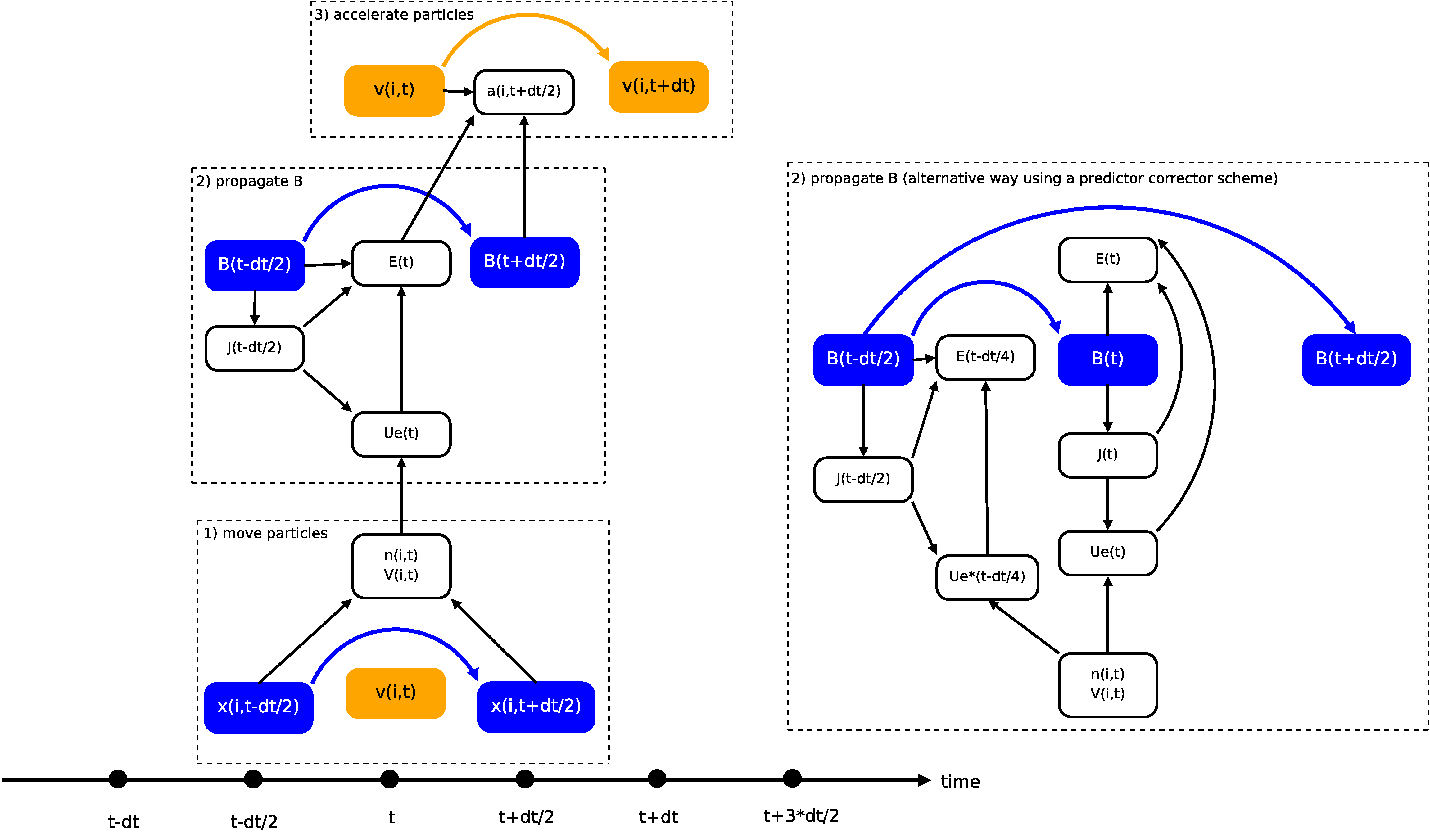
Leapfrog algorithm of the HYB code
Grid refinements
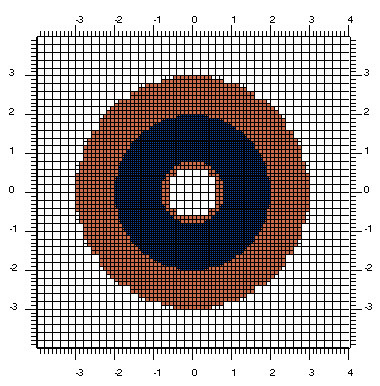
Hierarchically refined Cartesian 3-level mesh.
Grid refinements
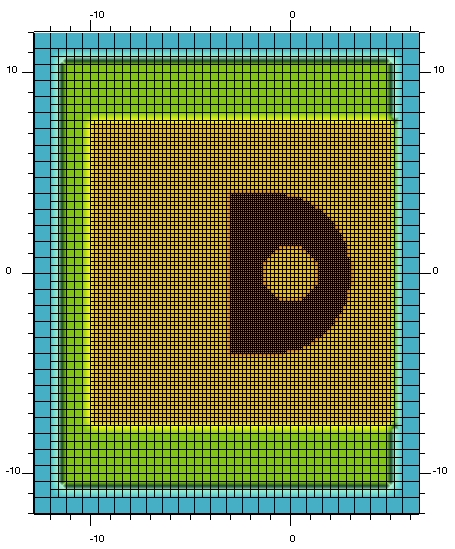
Hierarchically refined Cartesian 4-level mesh.
Constant grid
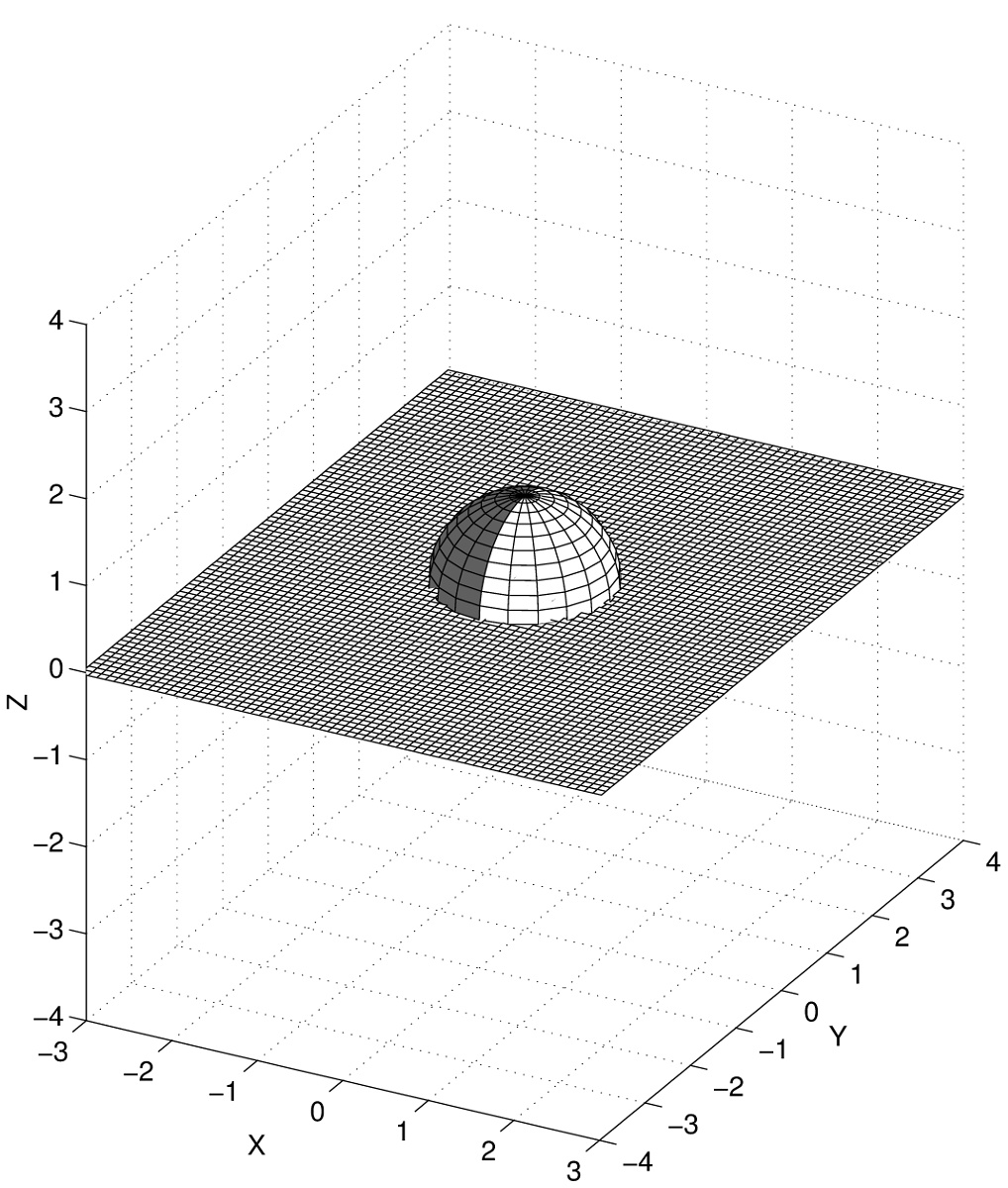
Cartesian simulation mesh with constant-sized grid cells.
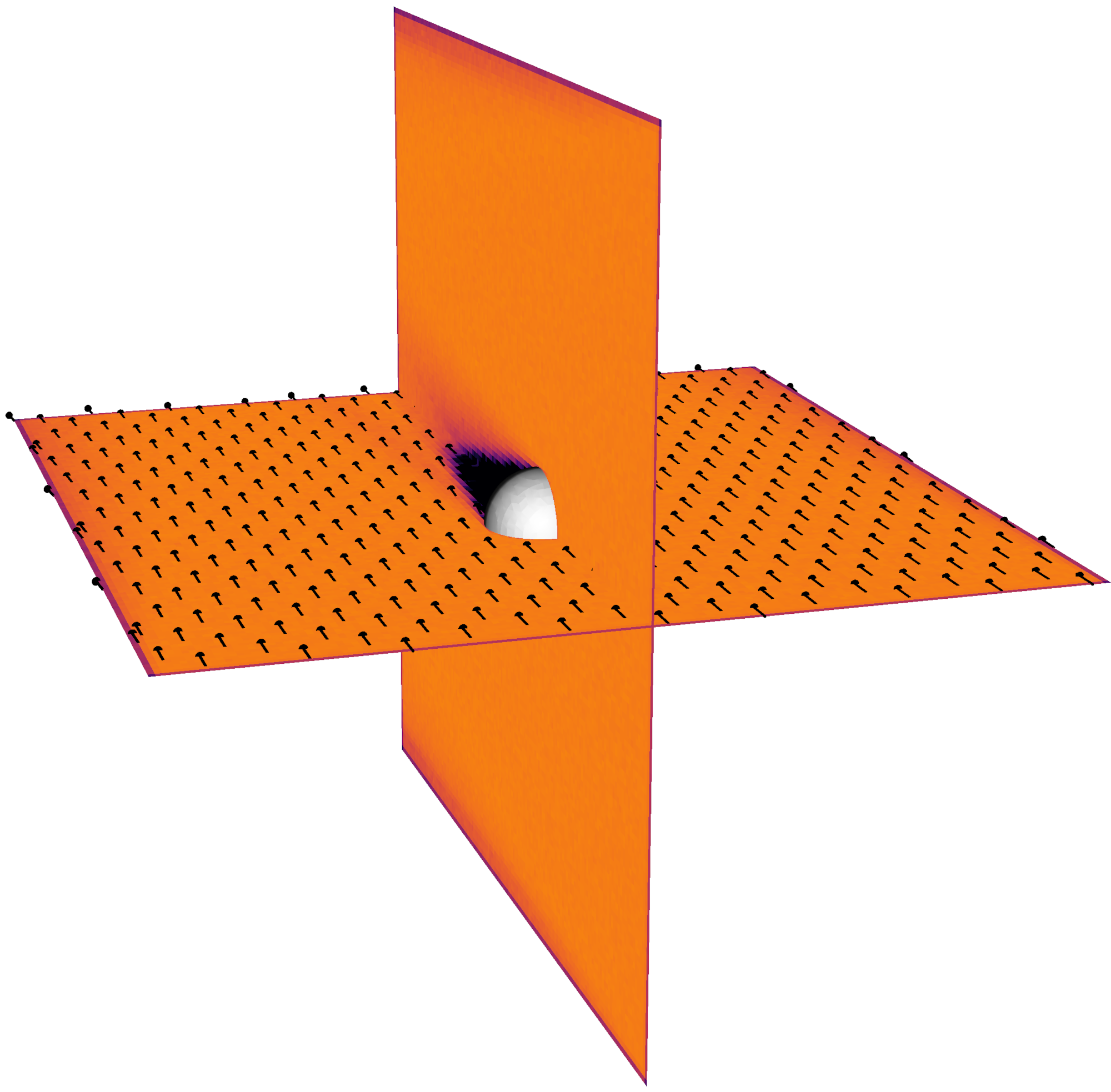
Laminar flow field
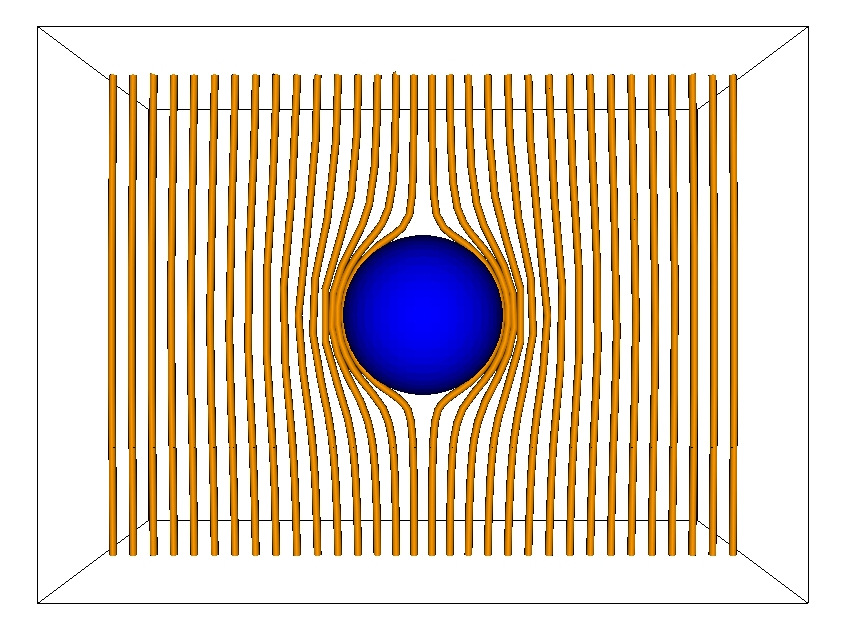
3D vector field corresponding to the magnetic field around a superconducting sphere in a homogeneous magnetic field (or the laminar flow around a sphere) used to initialize a flow-aligned magnetic field component with vanishing radial component at the inner boundary.
Hybrid Web Archive analysis tool
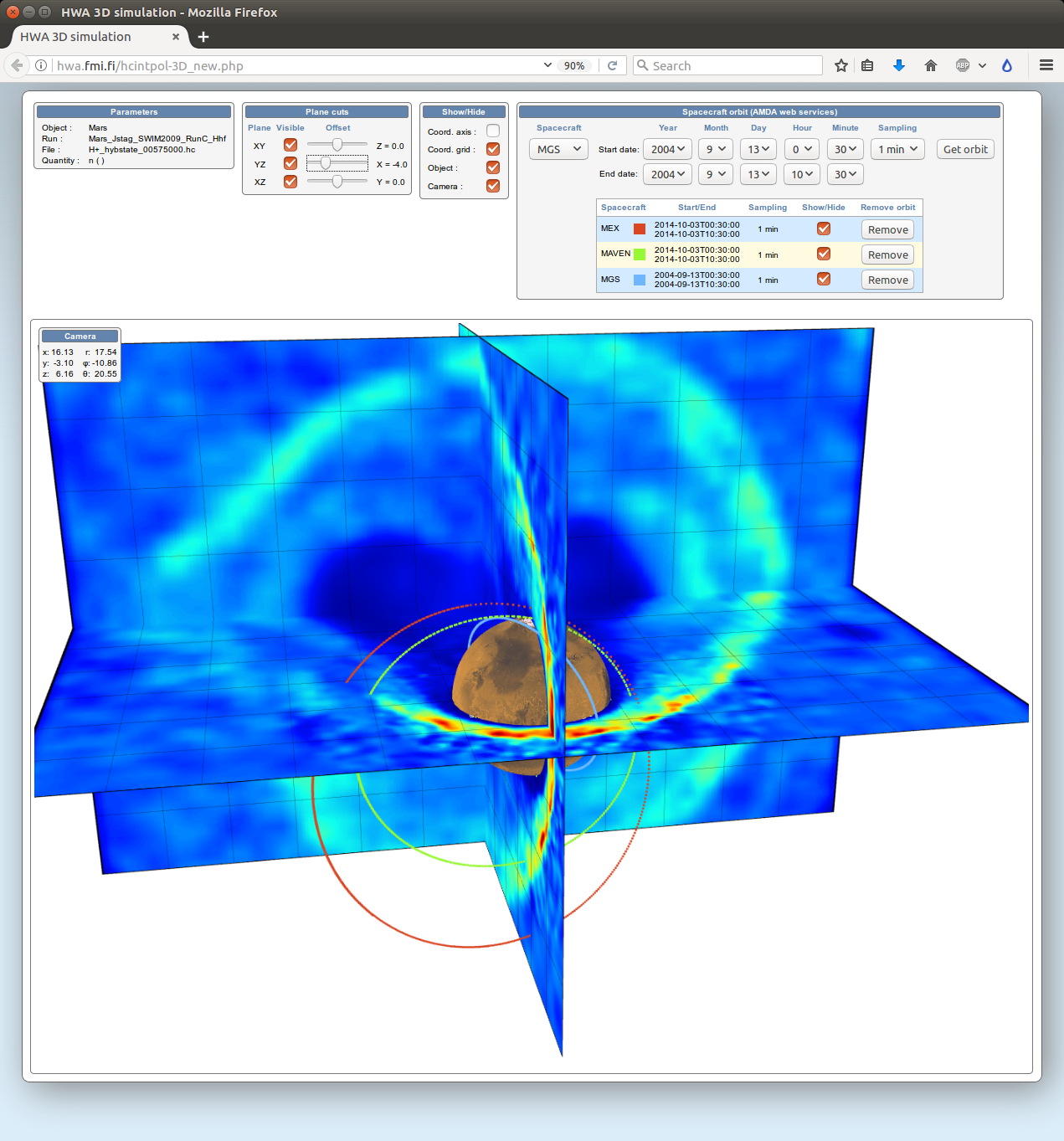
Analysis of a Mars simulation run on the Hybrid Web Archive (HWA).
© Finnish Meteorological Institute. All rights reserved. Design: HTML5 UP.